
Close

Approach Words: Comprehensive Management, Smart City, Sustainability
Public Policy Instruments: Communicative, Organization, Physical Intervention, Regulatory
The Domestic Solid Waste Management Centre (DSWMC) is the first and largest integrated waste treatment facility in the Middle East, located in Mesaieed in Doha. It plays a central role in Qatar’s waste management system by processing municipal solid waste while generating electricity,1 2 aligning with the goals of Qatar’s National Vision 2030 to enhance waste management strategy and promoting sustainable infrastructure.3
The project envisions a “sustainable and efficient waste management system” that maximizes resource recovery, minimizes environmental impact, and contributes to Qatar’s circular economy goals.4 By integrating waste-to-energy technology, recyclingand composting, the initiative supports clean energy generation and long-term waste sustainability. It aims to:5
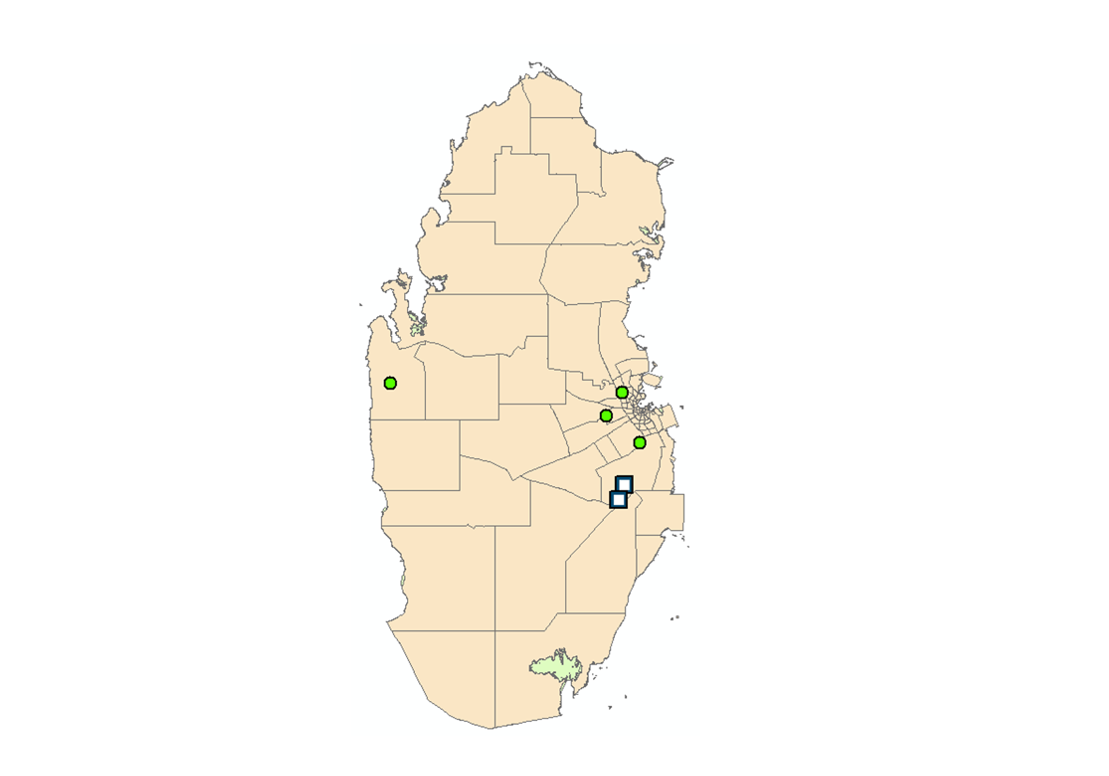
Title: WTS, the landfill and DSWMC on Qatar Map.
Source: Click Here

Title: DSWMC building in Mesaieed in Qatar.
Source: Click Here
Title: 3D drawing of the Geometric Dome of the DSWMC building.
Source: Click Here
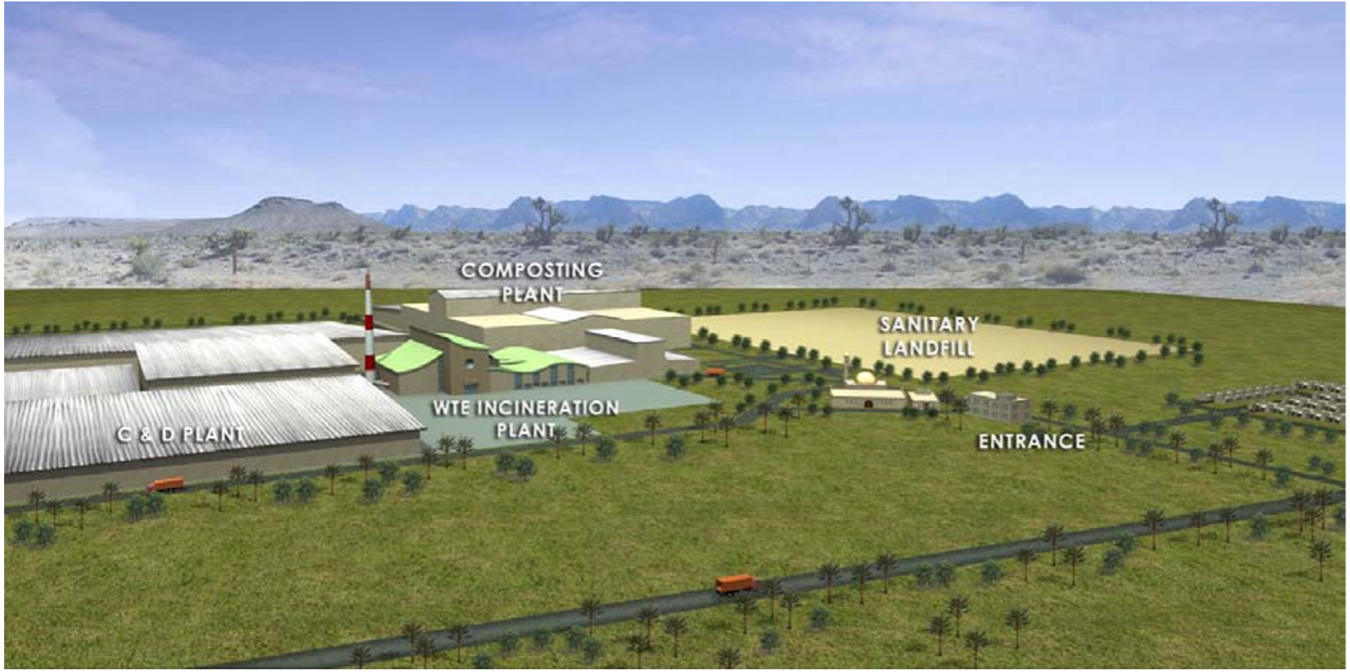
Title: Rendered drawing showing the facilities at DSWMC.
Source: Click Here
To achieve this vision, Qatar’s waste management strategy follows national sustainability policies and municipal regulations, including:
The DSWMC processes 2,300 tons of solid waste each day6 and produce 50 MW of electricity daily, supplying power to 47,000 homes.7 Equipped with advanced technologies for waste sorting, composting, and metals recovery, the facility successfully diverts 95% of processed waste from landfills.8 By reducing pollution and improving air quality, the project enhances environmental sustainability while increasing the share of renewable energy in Qatar’s national grid.9
The DSWMC benefits Qatar’s residents with improved waste disposal services, while the government and industry gain from reduced landfill reliance and enhanced resource recovery, advancing national sustainability goals. Additionally, the energy sector benefits from increased clean energy production, supporting Qatar’s transition to a more diverse and sustainable energy mix.
The Ministry of Municipality and Environment (MME),10 under the supervision of the Qatari Ministry of Municipality and Urban Planning (MMUP),11 oversees policy formulation and regulatory compliance for the Domestic Solid Waste Management Centre (DSWMC). Keppel Seghers, managed by Keppel Infrastructure Trust, serves as the facility’s developer and operator, handling daily operations.12 Private sector investors contribute to infrastructure development, while the Qatar Electricity and Water Company (QEWC) oversees grid integration.
The DSWMC was established in 2011.13 In 2022, it underwent expansion plans through introducing new waste management center to boost recycling and energy recovery. By 2030, Qatar aims to achieve a 25% renewable energy share, with waste-to-energy projects playing a crucial role in achieving this goal.14
Project Link
Endnotes
N.A.
References