
Close

Approach Words: Comprehensive Management, Efficiency, Sustainability
Public Policy Instruments: Financial Mechanism, Planning, Regulatory
The Sharjah Waste-to-Energy (WTE) Plant isa pioneering first of its kind commercial-scale WTE facility in Sharjah, the UAE and the broader Middle East.1 It was developed to aims to address municipal solid waste challenges while contributing to the region’s energy sustainability. It is a step towards positioning Sharjah as the first zero waste city2 and boosting UAE’s net-zero emissions in 2050 goals.3
The project envisions “integrating waste management with energy production, reducing landfill reliance while generating clean power”. It aims to operationalize circular economy principles by focusing on waste reduction, energy recovery, and carbon emissions mitigation.4 In doing so, it supports Sharjah’s zero waste-to-landfill goals and contributes to the UAE’s broader national sustainability agenda.5
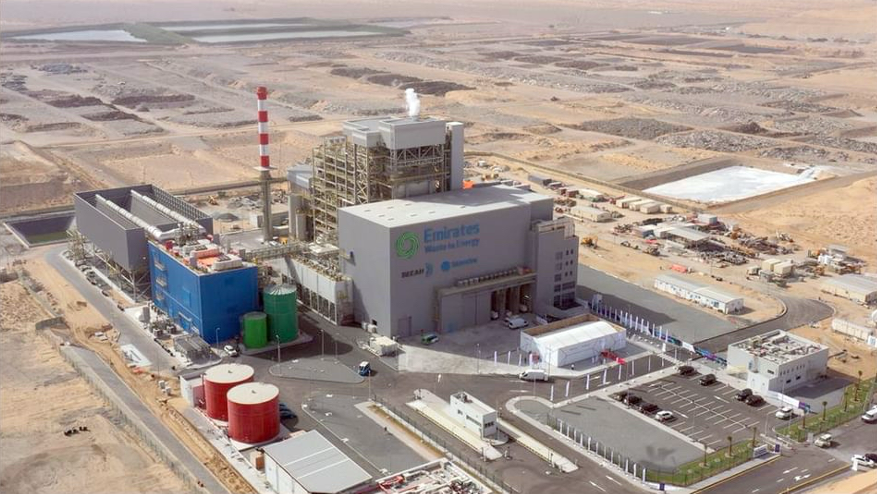

Title: Aerial view of the Sharjah WTE Plant.
Source: Click Here
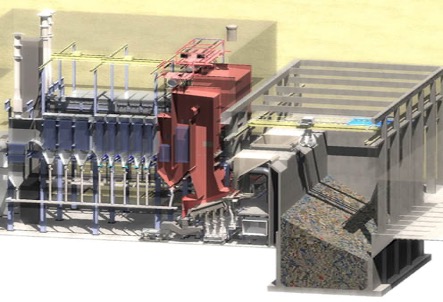
Title: A render of one of the facilities at the WTE plant.
Source: Click Here
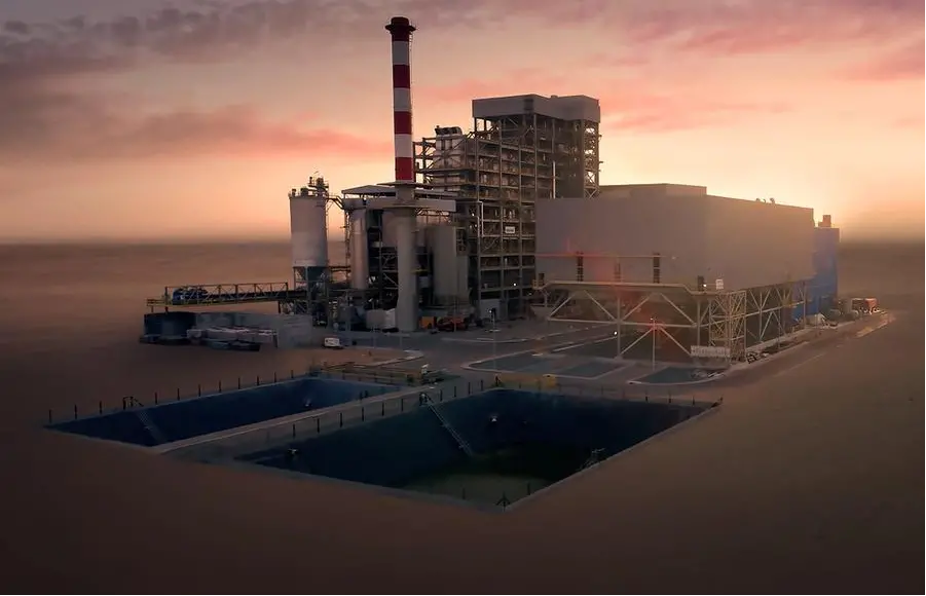

Title: Another render of the Sharjah WTE Plant.
Source: Click Here

Title: Facility’s technology machineries.
Source: Click Here
Spanning 80,000-square-meter,6 the facility is designed to process up to 300,000 tonnes of non-recyclable waste annually, producing almost 30 MW of electricity, supplying around 28,000 homes with power.7 The plant helps prevent 450,000 tonnes of CO2 emissions, saves around 45 million cubic meters of natural gas yearly, and diverts waste from landfills.8
The facility embodies an all-inclusive sustainable waste management approach by integrating waste-to-energy conversion with air pollution control measures and ensuring efficient resource recovery through the separation and reuse of recyclable materials.9 In alignment with strict EU environmental standards, particularly in flue gas treatment, the plant operates with high environmental and operational performance.10
Using advanced WTE technologies, the plant employs high-temperature and high-pressure steam for incineration and heat recovery, which is then used to drive turbnes for electricity generation. This process not only maximize resource efficiency but also minimize environmental impact.11 12
The plant benefits Sharjah residents by providing cleaner energy, reducing landfill dependency, and improving air quality.13
Developed as a joint venture between Bee’ah and Masdar,14 15 the project involves key stakeholders, including the Government of Sharjah and international and financial institutions that include the Abu Dhabi Fund for Development, Standard Chartered Bank, and Siemens Financial Services.16
Sharjah WTE Plant was inaugurated in 2021,17 with commercial operations beginning in the third quarter of the same year after successful construction and commissioning phases.18 Future expansions are planned across the UAE and the broader Middle East, advancing the region’s waste-to-energy capacity.19
Project Link
https://masdar.ae/en/renewables/our-projects/sharjah-waste-to-energy-project
Endnotes
N.A.
References