
Close

Approach Words: Comprehensive Management, Integrated City, Sustainability
Public Policy Instruments: Communicative, Organization, Planning, Regulatory
Environmental Monitoring Information System of Kuwait (eMISK) is a comprehensive initiative for collecting, analyzing, and distributing environmental information across various zones in Kuwait.1 It aims to improve environmental governance and public awareness by providing reliable data that supports decision-making.2
eMISK’s envisions “turning Kuwait into an environmental leader in knowledge and management”.3 It upholds directness and data driven decision making by providing stakeholders and the public with real-time environmental data. Through this, it empowers stakeholders and the public to actively engage in sustainability efforts.4
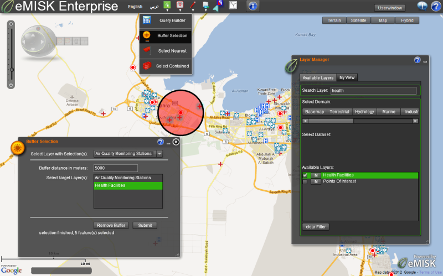
Title: buffer analysis showing health facilities near air quality stations.
Source: Click Here
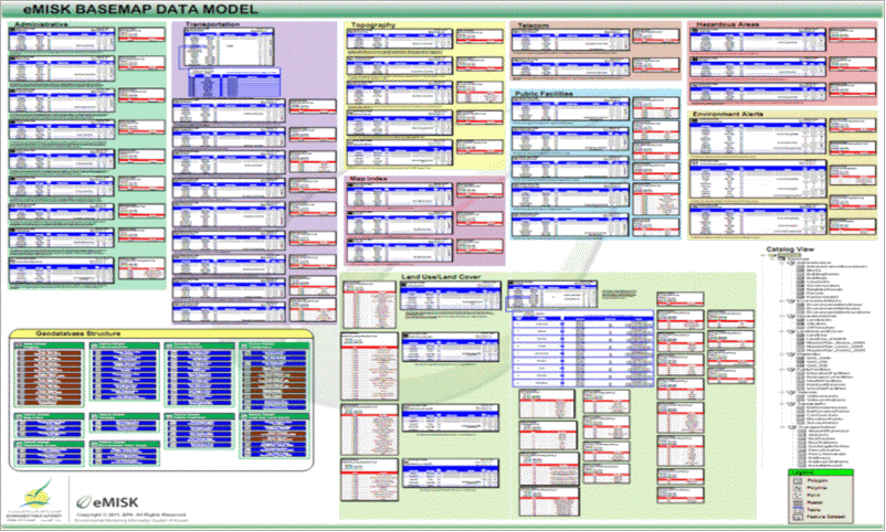
Title: eMISK Base Map Field Data Model of Kuwait’s evolving geo-environmental landscape.
Source: Click Here
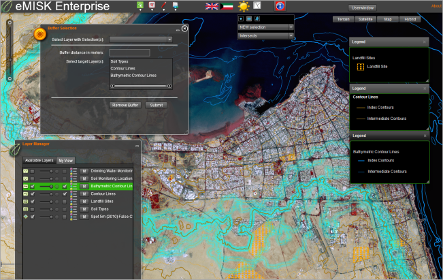
Title: eMISK Enterprise Spatial Analysis.
Source: Click Here

Title: EPA’s President’s Award for Executive Leadership in 2012.
Source: Click Here
To implement its vision, it employs a strategic plan that develops a comprehensive environmental infrastructure. This includes an internal data management system, geo-environmental database and public portals like “Beatona”.5 The plan ensures data and policies are updated and informed accurately, monitored and reported to ensure stakeholder engagement.6 It directly addresses environmental challenges like resource depletion, pollution, and habitat harm.7
Covering the entire Emirate of Kuwait, eMISK incorporates data from several regions for a whole assessment of the environmental status.8 Forming the environmental database, the system encompasses 11 environmental sectors:9
(1) Water
(2) Air
(3) Soil
(4) Sea
(5) Industry
(6) Transportation and Waste
(7) Energy
(8) Oil and Gas
(9) Population
(10) Biodiversity
(11) Base Map
Further, it integrates spatial analysis tools to visualize mobility patterns, aids transportation planning, and environmental impact assessments.10 The platform also offers access to information regarding public spaces and facilities, guaranteeing that environmental considerations are unified within urban development and management.11
Kuwaiti locals benefit from eMISK via gain accessibility to environmental information, ongoing initiatives, improved conditions, as well as being updated on waste management policies.12 Governmental entities, on the other hand utilize eMISK for policymaking, regulation enforcement, and development. Researchers rely on eMISK for studies and analyses, while the public gains awareness and opportunities to participate in environmental protection efforts.13

Owner/Developer (Public)

Funder

Contractor/Implementer
eMISK was initiated in 2011 by Kuwait’s Environment Public Authority (EPA) overseeing policies and regulations,14 and has undergone 3 main phases:15 16
For eMISK project, EPA received multiple prizes from ESRI; GISRA Prize (2010), GIS Achievement Award (2010), Leadership Award for Entrepreneurship (2011) and President’s Leadership Award (2012), for the GIS environmental involvement and data management.17 Additionally, eMISK won the ICT’s World Summit Award for the Information Society (WSIS) in 2016 in Geneva, for its scientific impact, its Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) integration, and its innovative monitoring using GPS, GIS, and remote-sensing tools.18
Project Link
https://epa.gov.kw/en-us/eMISK
Endnotes
N.A.
References