
Close

Approach Words: Smart City, Sustainability, Urban Livability
Public Policy Instruments: Financial Mechanism, Organization, Physical Intervention, Planning, Regulatory
Msheireb Downtown project is a mixed-use development project1 revitalizing the old commercial heart of Doha. The project is situated near Souk Waqef, Amiri Diwan (Qatar’s seat of government), and just minutes away from Hamad International Airport. It is designed to be one of the most sustainable and smart districts in Doha, aspiring to emerge as a new destination for living2, leisure, and business3. The project adopted traditional Qatari architectural language with modern technology4, aiming to preserve both environmental sustainability and Qatar’s cultural identity. The goal is to “bring people back to their roots5, rediscover a sense of community and togetherness.” Msheireb Downtown is part of Qatar National Vision 2030i ” to transform Qatar into a country capable of sustaining its own development and providing a high standard of living for generations to come”6.
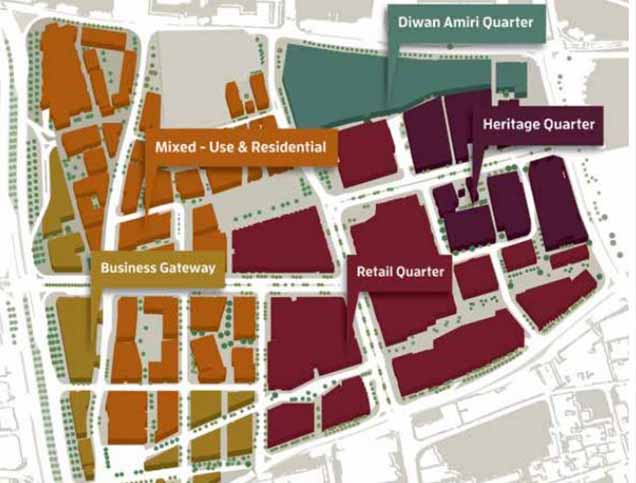
Title: Five quarters in the Msheireb Downtown Master Plan.
Source: Click Here

Title: Character Zones of Msheireb Downtown.
Source: Click Here
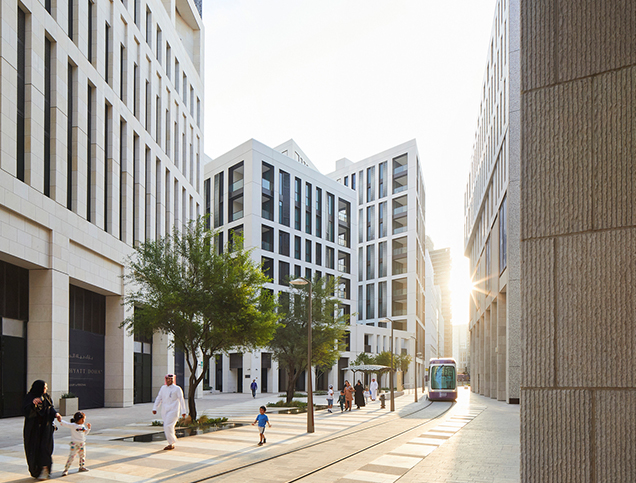

Title: Picture showing the tram inside Msheireb Downtown between the pedestrians.
Source: Click Here
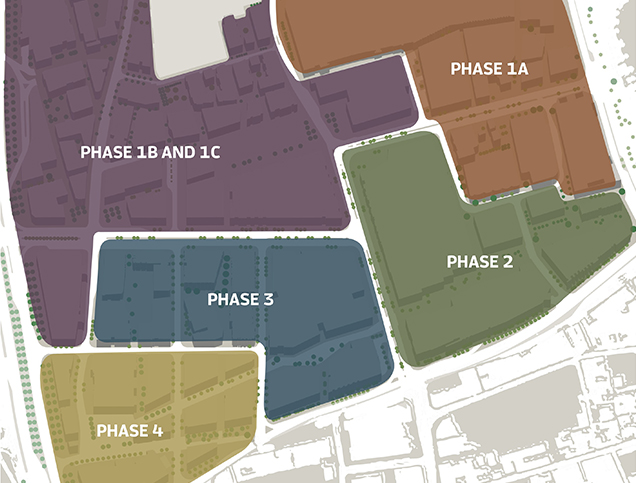
Title: Phases of construction.
Source: Click Here
To implement the project objectives, a master plan7 was proposed for an area of 0.31 square kilometer8. The plan is composed of five main quarters forming a mixed-use district9. Specifically, it includes over 800 residential units, 193,000 sqm commercial space10, more than 300 retail shops, 4 hotels, 4 heritage house museums, 1 school and 3 mosques, with parking spaces for over 10,000 vehicles. In terms of mobility, the project was designed as a walkable district with streets planned to provide shade from the sun and capture cool breezes from the Gulf11. A tram system powered by clean energy, along with dedicated bicycle and pedestrian lanes, are also included to facilitate accessibility and connectivity between all quarters within the district.
In terms of sustainability, the development is designed to reduce energy usage by 30% through enhanced building envelope efficiency12. It heavily utilizes renewable energy, with over 6,400 rooftop solar panels installed to generate electricity. Non-potable water consumption is reduced by 70% of the city’s total consumption13 14. Smart infrastructure systems are also incorporated, such as automated waste collection system that separates recyclables15. The entire development is LEED Gold or Platinum certified, meeting stringent sustainability benchmarks.

Owner/Developer


Funder
The project is initiated by the real estate company Msheireb Properties16, a subsidiary of Qatar Foundation for education17, sciences and community development; which specified the master plan18 for the project done by a team of 4 companies comprised of Arup (lead consultant), AECOM, and Allies and Morrison19 20. The project is funded by Qatar Foundation with an approximate cost of billion US$5.5 billion21 22.
The project was constructed between 2010 and 2021 in four phases by several contractors23 as follows:
Project Link
Endnotes
References