
Close

Approach Words: Integrated City, Sustainability, Urban Livability
Public Policy Instruments: Financial Mechanism, Organization, Physical Intervention, Planning
The Tangier City port redevelopment project1 transforms Tangier’s old cargo port into a modern, mixed-use waterfront development with cruising and yachting facilities.2 This transformation was accompanied by the opening of the New Tangier Med Port,i which shifted industrial activities away from the old port between 2006 and 2010 and freed it from cargo transport operations.3
The project is guided by two main visions: “Bringing the sea to the city” and “Uniting the port with the city”.4 Hence, the project aims to integrate the historic Medina neighborhood with its coastline5 and transform the area into a vibrant tourist destination6 by creating a dynamic mixed-use development accessible to all,7 and establishing an international hub for cruising and yachting tourism.8
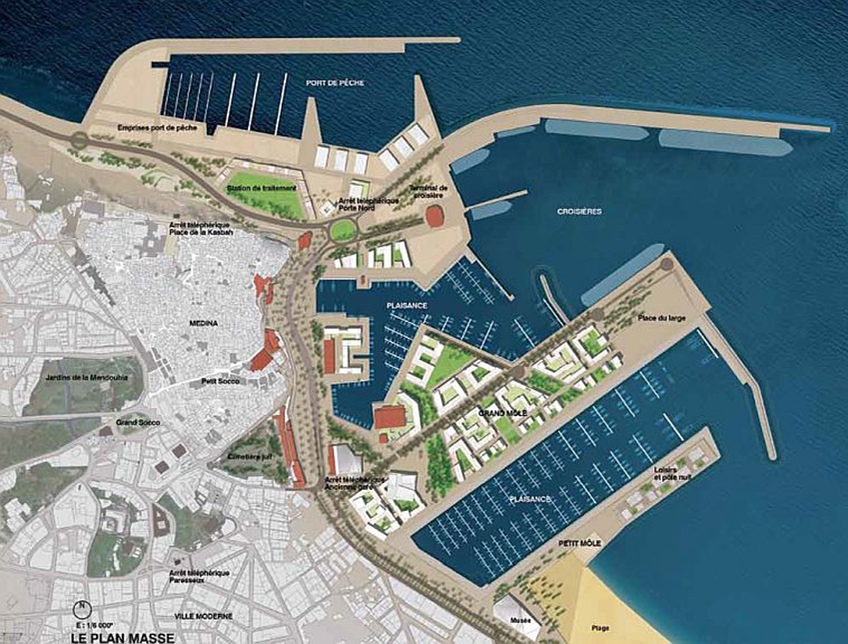
Title: Master Plan of the Tangier Ville Port Project.
Source: Click Here
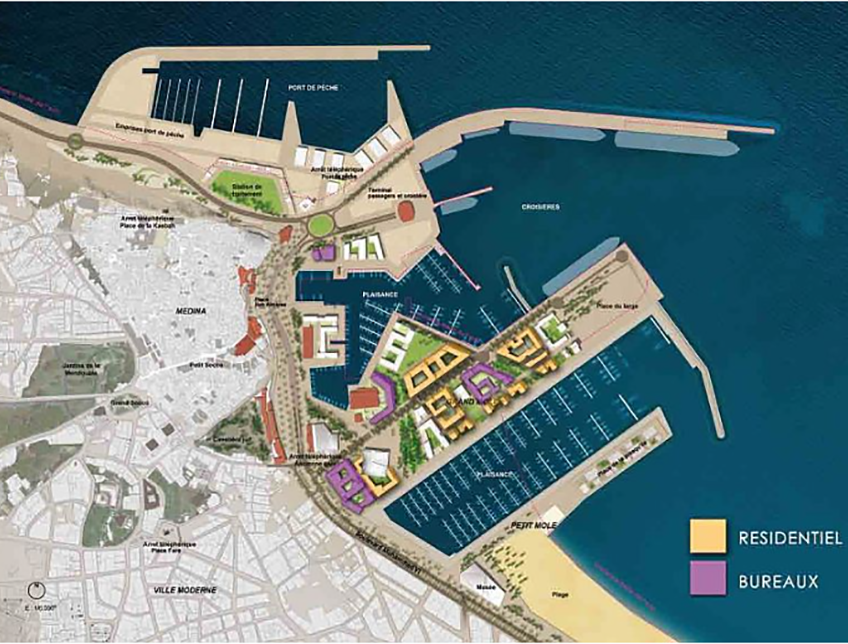
Title: Land Use Plan.
Source: Click Here
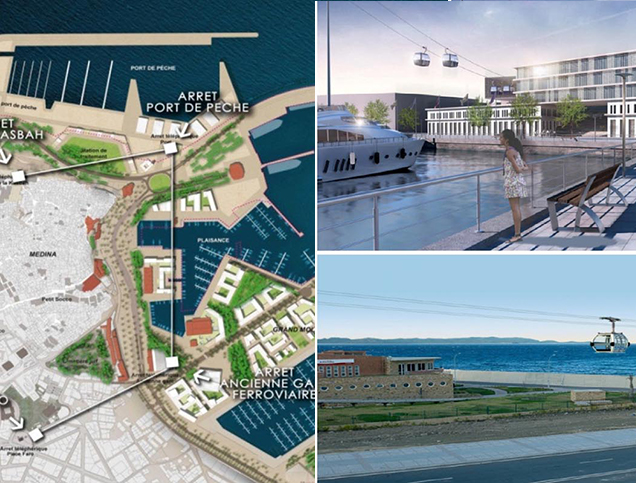
Title: Cable Car Transportation System.
Source: Click Here
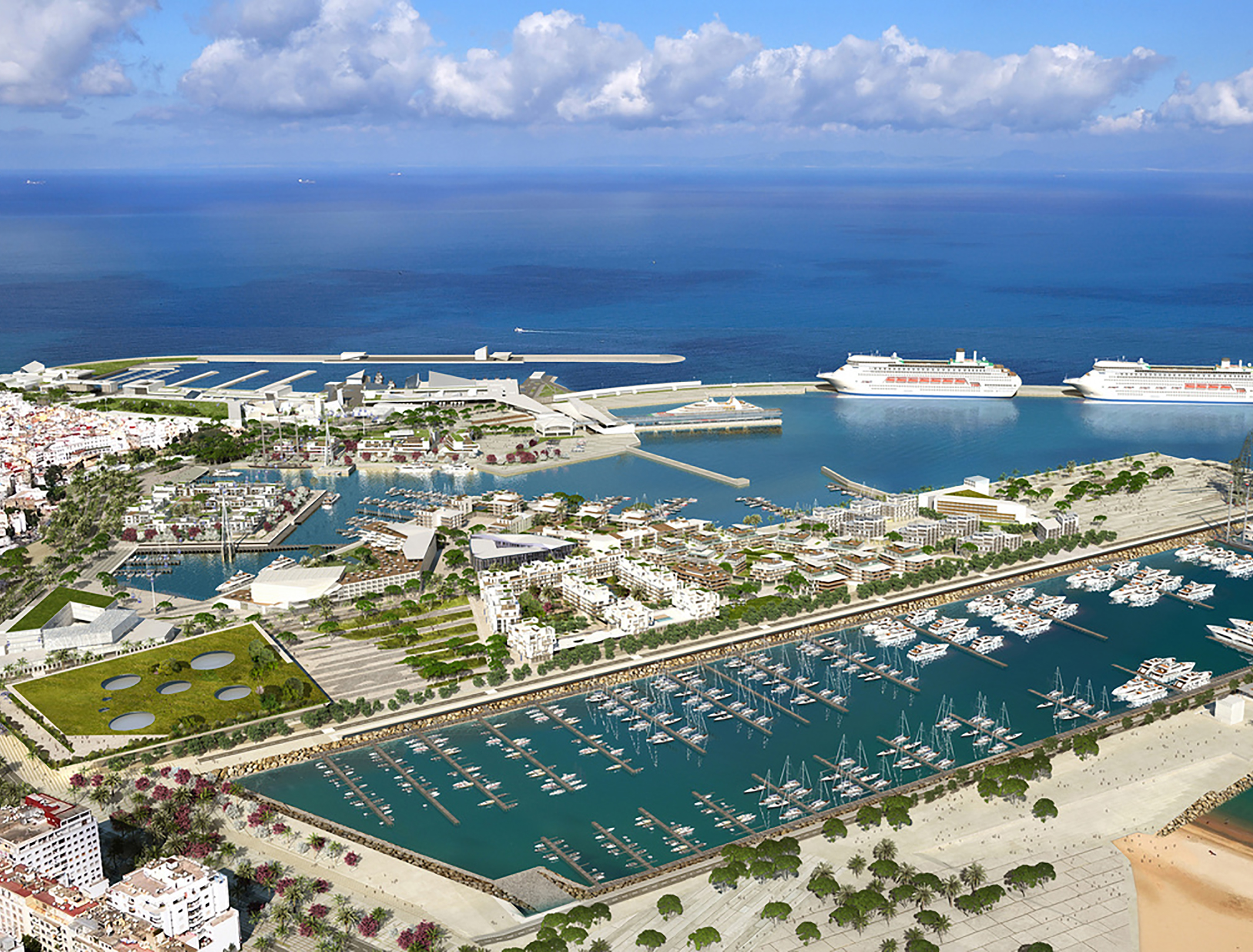

Title: Three-dimensional view of the project.
Source: Click Here
To implement these objectives, a comprehensive master plan was developed for an area of 1.6 square kilometers9 in Tangier’s city center, adjacent to the old Medina.10 The plan divides the project into two main zones: the port zone, spanning 0.76 square kilometers,11 and the urban zone, covering 0.84 square kilometers.12 The main land use components of each zone in the master plan are as follows:
The urban zone consists of:
The port zone comprises several key components:
To enhance accessibility, the project includes a cable car transportation system.29 This system will handle 2,800 passengers per hour over a 2-kilometer distance, connecting the Kasbah, cruise terminal, marinas, and Place Faro.30

Consultant/Designer
It is worth noting that the development has been certified by the National Environmental Impact Evaluation Commission,ii ensuring that site development activities will be environmentally friendly. For instance, sand dredged during the new marina construction will replenish various beaches in the Bay of Tangiers. The vegetation system in the reconverted port will feature species adapted to Tangier’s bioclimatic characteristics.31 Moreover, iconic buildings in the port area will be restored and repurposed to preserve the existing atmosphere, while nearby monuments will be enhanced.32
The “Tanger City Port Development Society” (SAPT)33 initiated the project in 2010.34 SAPT’s principal shareholders include the State of Morocco, the Hassan II Fund for Economic and Social Development, the City of Tangiers, the National Ports Agency (ANP), and the Agency for the Promotion and Economic and Social Development of the Northern Provinces of Morocco.35 SAPT (49% owned) and ANP (51% owned) created a joint venture company called “Tanger City Port Management Company” (SGPTV),iii responsible for developing infrastructure and managing operations for cruise, recreational sailing, and ferry activities under a fifty-year concession agreement.36 The project’s master plan was designed by the consulting firm Carta – Reichen Et Robert Associés.37 The project’s total cost is estimated at over $632 million, primarily funded by the state of Morocco, Hassan II Fund for Economic and Social Development.
Project Link
https://www.tangerport.com/language/en/the-project/
Endnotes
References