
Close

Approach Words: Smart City, Sustainability, Urban Livability
Public Policy Instruments: Financial Mechanism, Physical Intervention, Planning
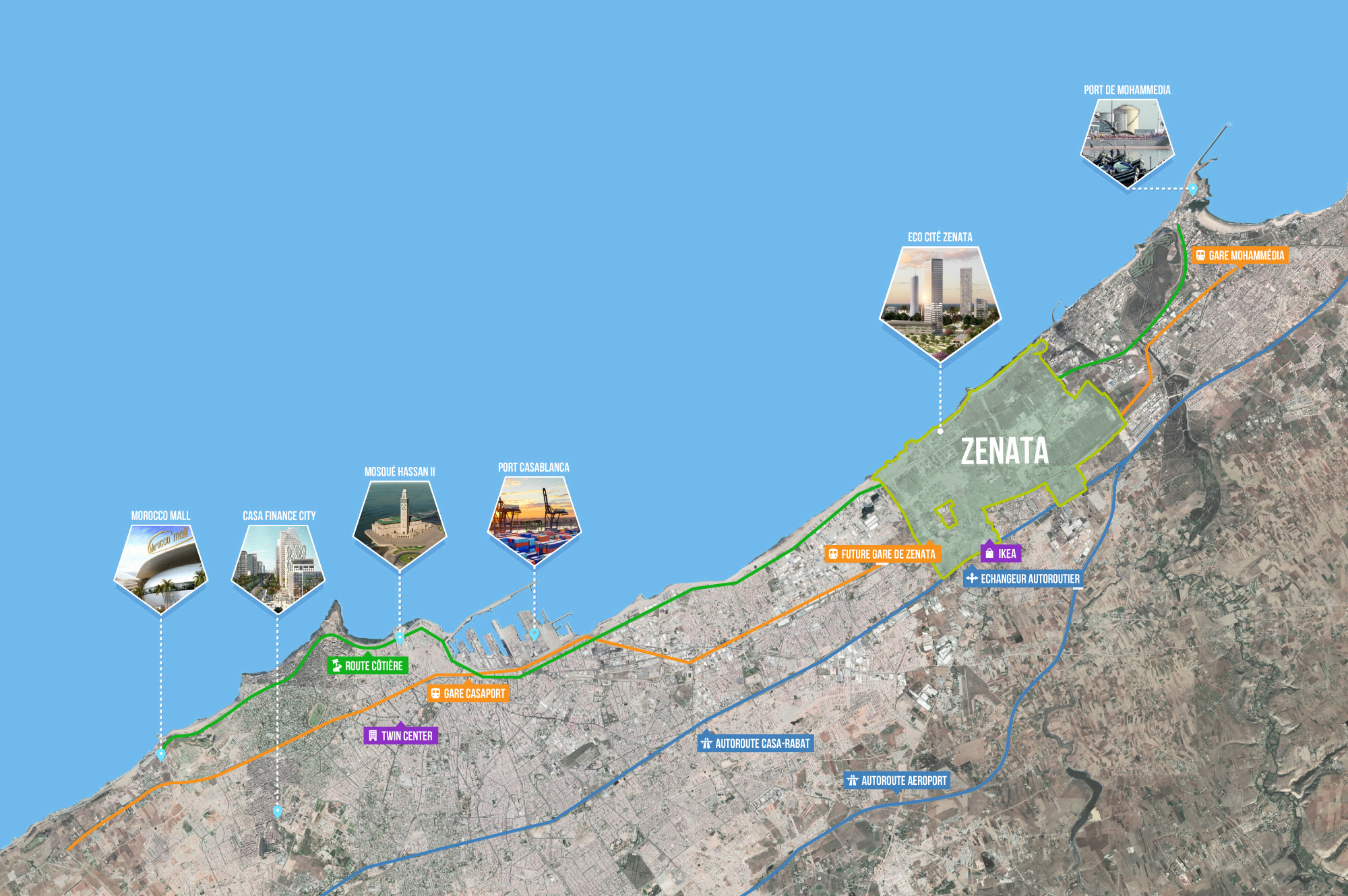
Zenata Eco-City is a sustainable, mixed-use urban development project1 located in the northeastern part of Casablanca.2 Strategically positioned at the crossroads of Morocco’s two largest cities, Rabat, the administrative capital, and Casablanca, the economic capital,3 it is the first eco-city in Morocco4 and the first African city to receive the Eco-City Label (ECL).i 5
The project emerges as a response to the rapid urbanization and population growth in the Casablanca metropolitan area.6 As part of Morocco’s national program launched in 2004 to establish 15 new cities by 2020, Zaneta aims to address the urban challenges of Casablanca, a city marked by stark contrasts between its affluent, modern western areas and the industrial, isolated, and impoverished eastern districts.7
Zaneta Eco-City is designed to achieve two main objectives: ‘Urban expansion and housing solutions’; providing essential housing8 9 for approximately 300,000 inhabitants,10 to mitigate Casablanca’s housing shortage and reduce the prevalence of slums. And ‘sustainability and smart city innovation’; integrating eco-city principles with smart city technologies to create an efficient, livable urban environment that reflects the Moroccan lifestyle within an innovative framework.11
Title: Zenata City Location in Casablanca
Source: Click Here
Title: Zenata City Master Plan.
Source: Click Here
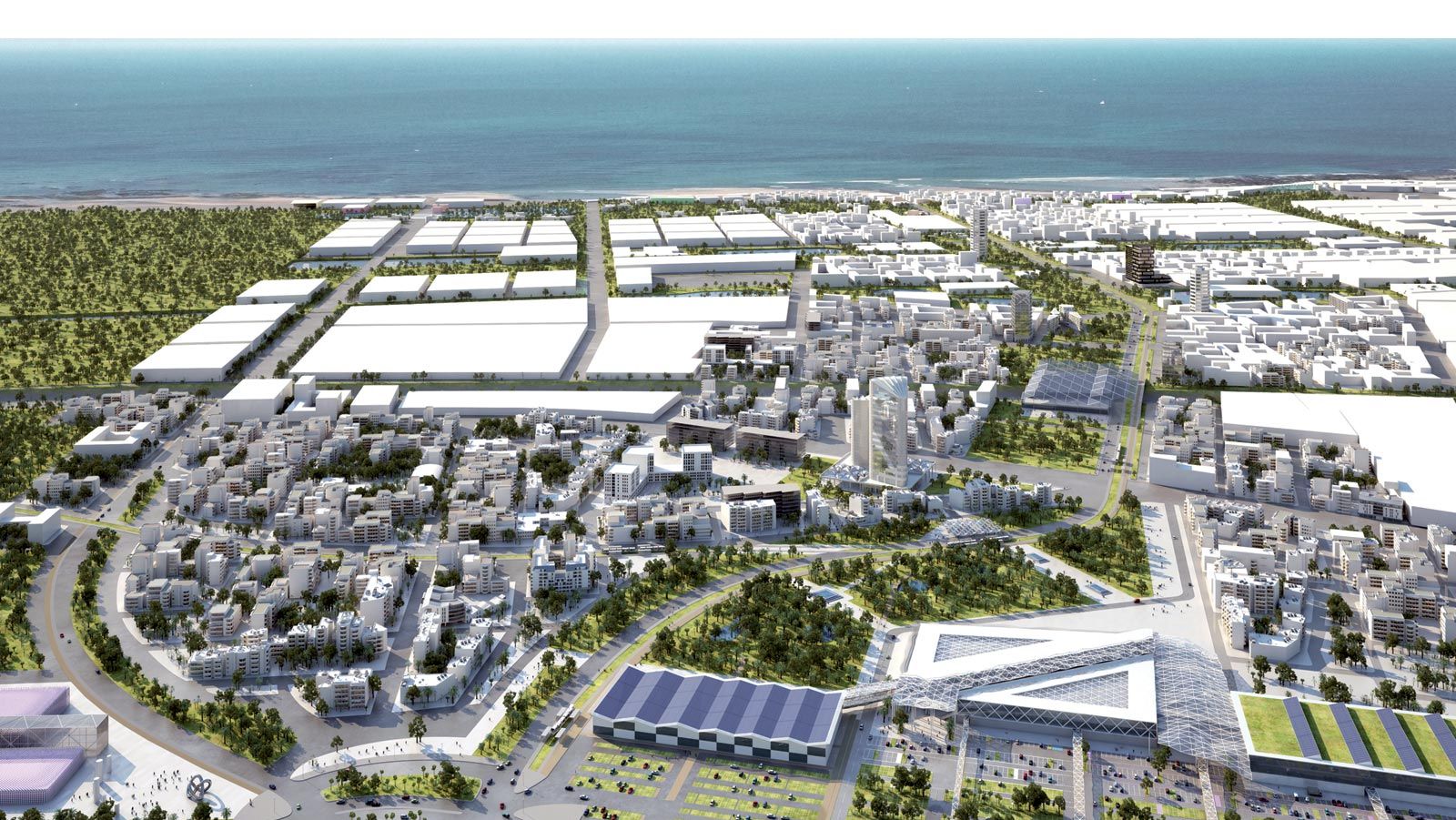

Title: 3D View of the project
Source: Click Here
Title: 3D View that Shows One of the Residential Neighborhoods of the Project
Source: Click Here
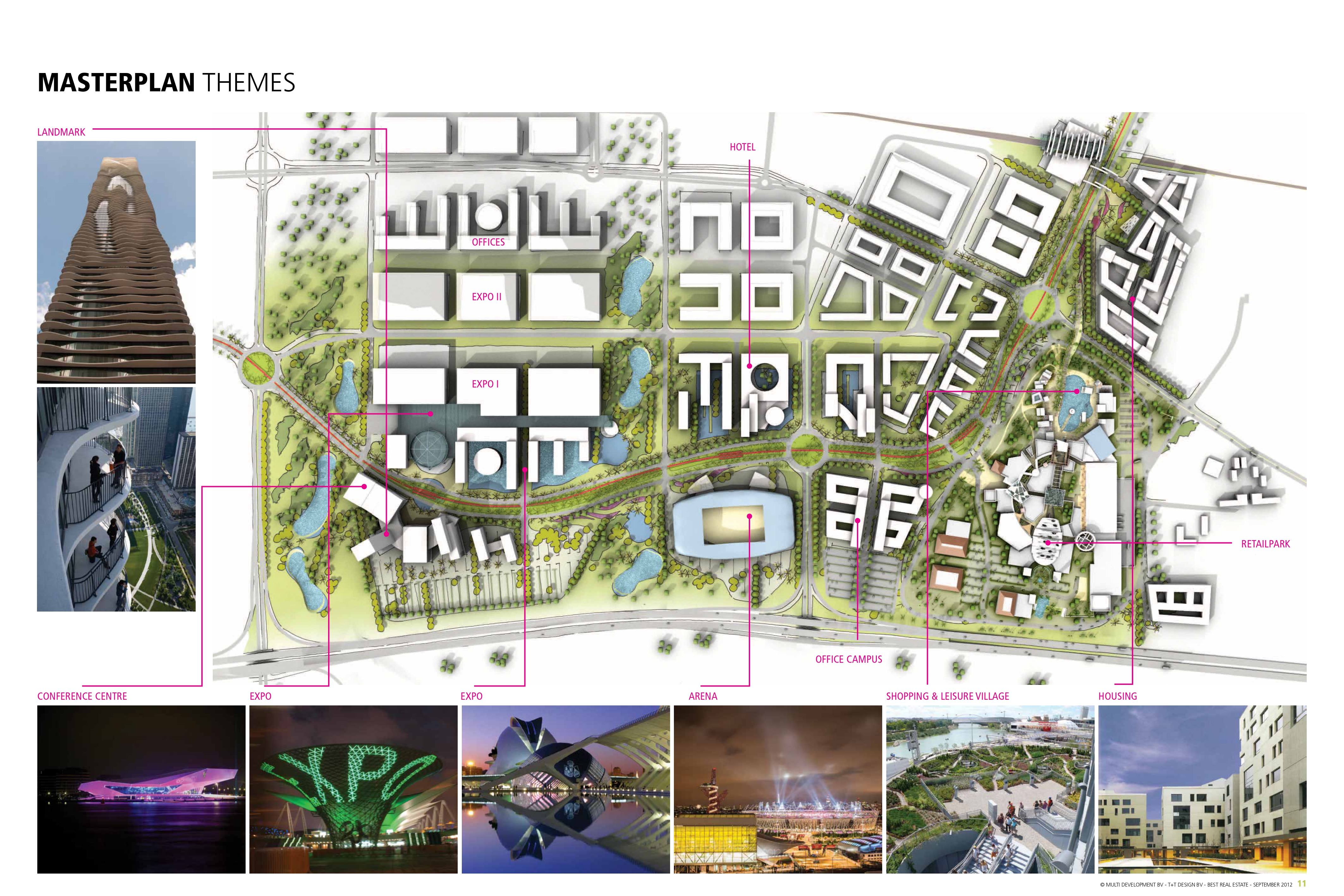
The master plan of Zenata eco-city covers an area of 18.3 square kilometers,12 extending over 5.35 kilometers along the Atlantic coast and 3.5 kilometers inland to the highway.13 It includes:
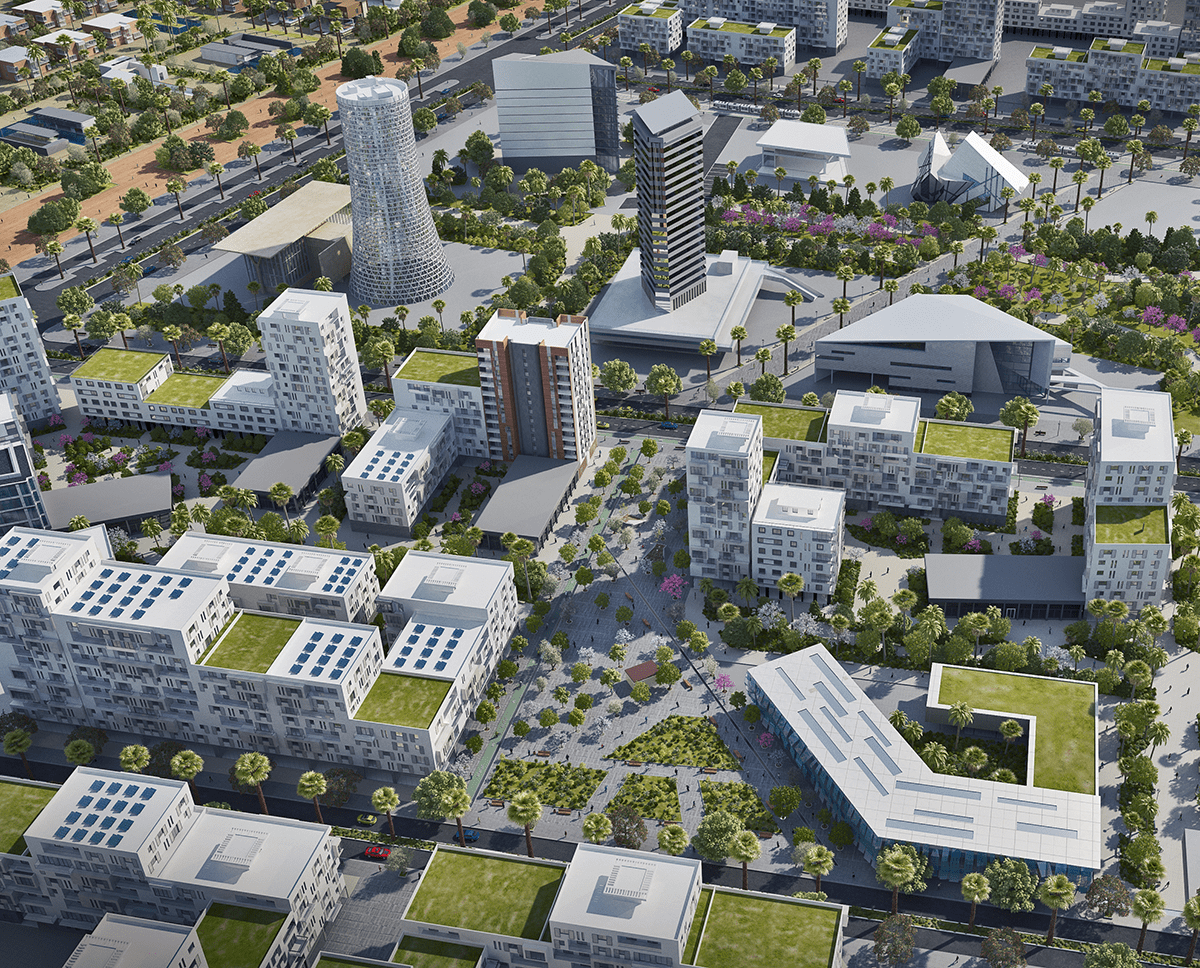
The Eco-city Zenata is a city designed for the well-being of its residents. Parks and green spaces are interwoven with the urban structures.22 Water retention basins aid groundwater recharge and support site afforestation efforts. These naturally irrigated parks, stretching to the sea, are designed as “ecological corridors.”23
The industrial park at Zaneta aims to optimize the consumption of energy and water, and to reduce liquid and solid waste – both at the residential and industrial levels.24
Zenata aspires to generate 100,000 jobs across high-value-added sectors including the commercial center, exhibition center, education and healthcare, logistics, tourism, light industry, municipal services, etc. These developments will not only boost the economy but also attract investments.

Owner/Developer (Public)

Consultant/Designer

Contractor/Implementer
The project was delegated to the “Caisse de Dépôts et de Gestion” (CDG Group) through a memorandum of understanding signed under the auspices of King Mohammed VI on February 11, 2006.25 CDG established the Zenata Development Company (SAZ) to oversee the overall design and implementation development.26 The master plan was designed by Reichen et Robert Associés.27
The total cost of the project is $2.2 billion,28 funded by the Moroccan government through loans from the European Union (EU) ($4.3 million), French Development Agency (AFD) ($163 million), and European Investment Bank (EIB) ($163 million).29 30
The development work at Zenata city began in 2016 and is planned for completion over a 10-year period.31 Key milestones include:
Project Link
Endnotes
References