
Close

Approach Words: Environment Preservation, Heritage Preservation, Urban Livability
Public Policy Instruments: Organization, Physical Intervention, Planning
The Qur’anic Botanic Garden (QBG) is a public educational garden that showcases plants mentioned in the Qur’an and the native flora of Qatar.1 Its vision is “to become a global hub for plant resource knowledge, education, and research, promoting cultures’ communication, environmental responsibility, and integrating preservation efforts with modern scientific achievements.”2
Specifically, the QBG aims to promote knowledge about plants mentioned in the Qur’an and Sunnah, their associated botanic terms, and their care and preservation methods.3 It also seeks to raise awareness about environmental conservation and sustainable gardening practices.4 The QBG project aligns the vision and goals of the Qatar Foundation (QF),5 i and the Qatar National Vision 2030.6 7 ii
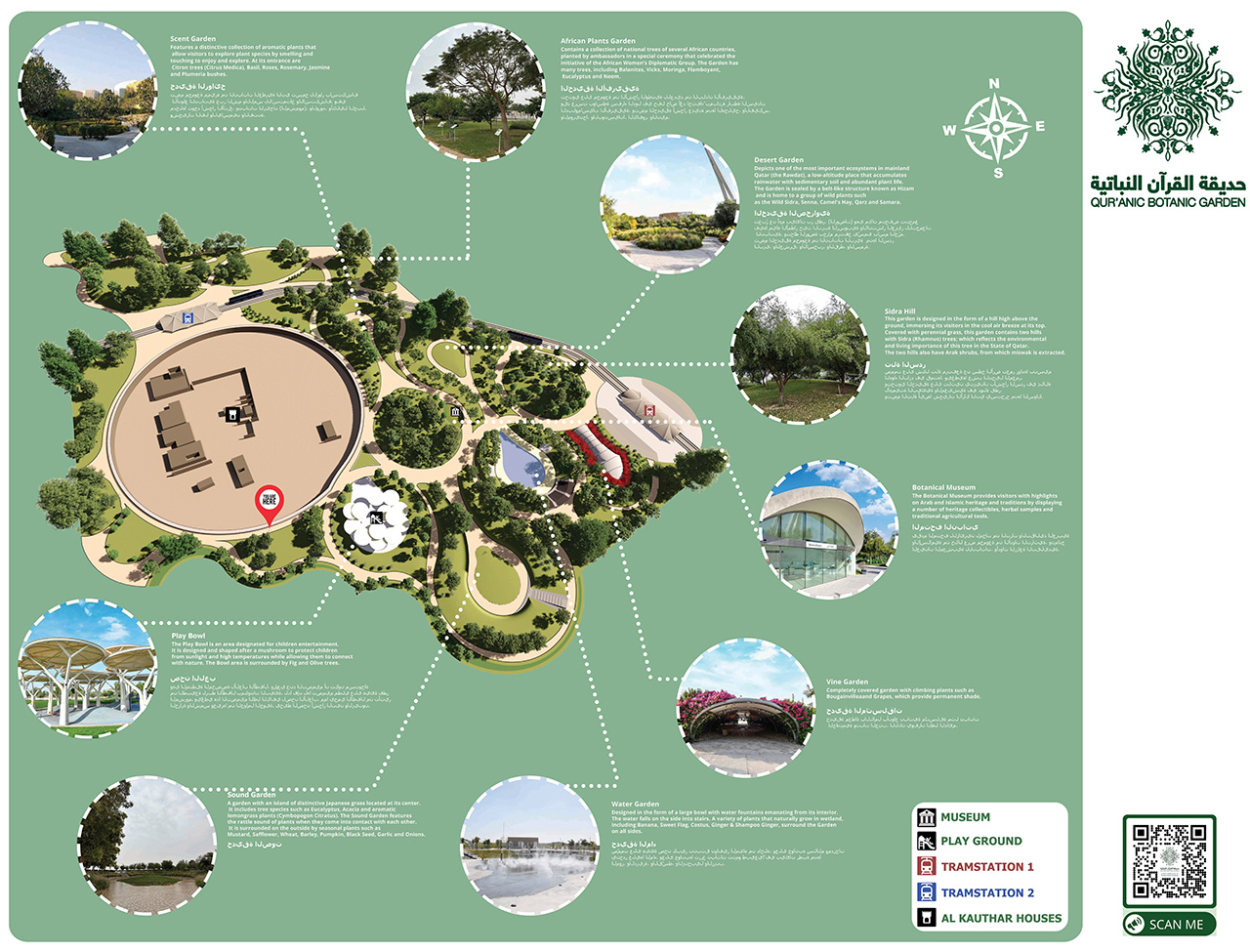
Title: An aerial 3D rendering of QBG showing the site’s components.
Source: Click Here
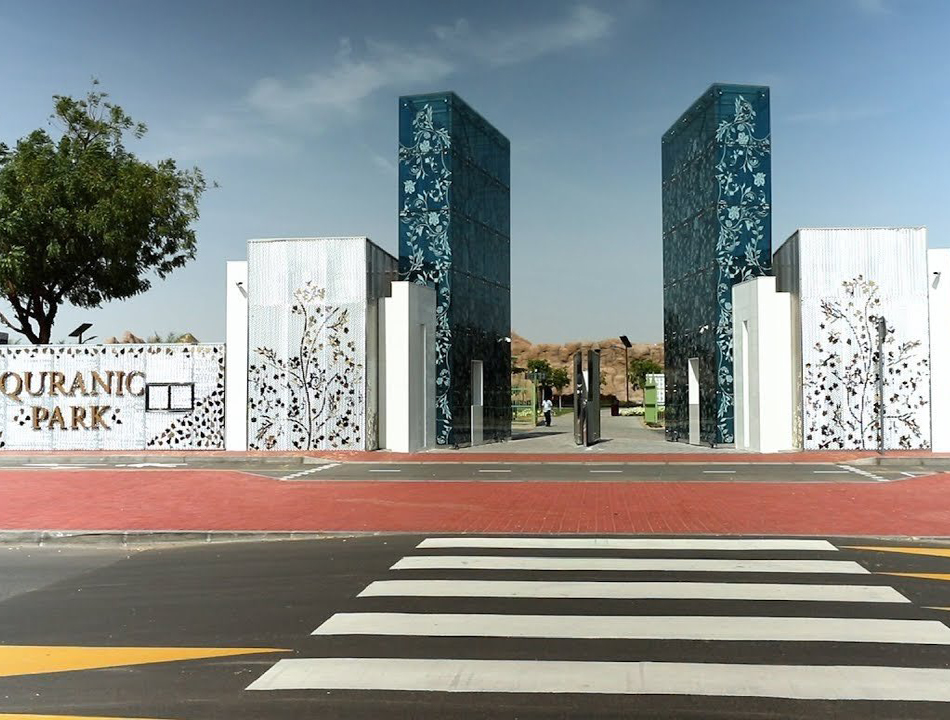

Title: Entrance of the Qur'anic Botanic Garden.
Source: Click Here
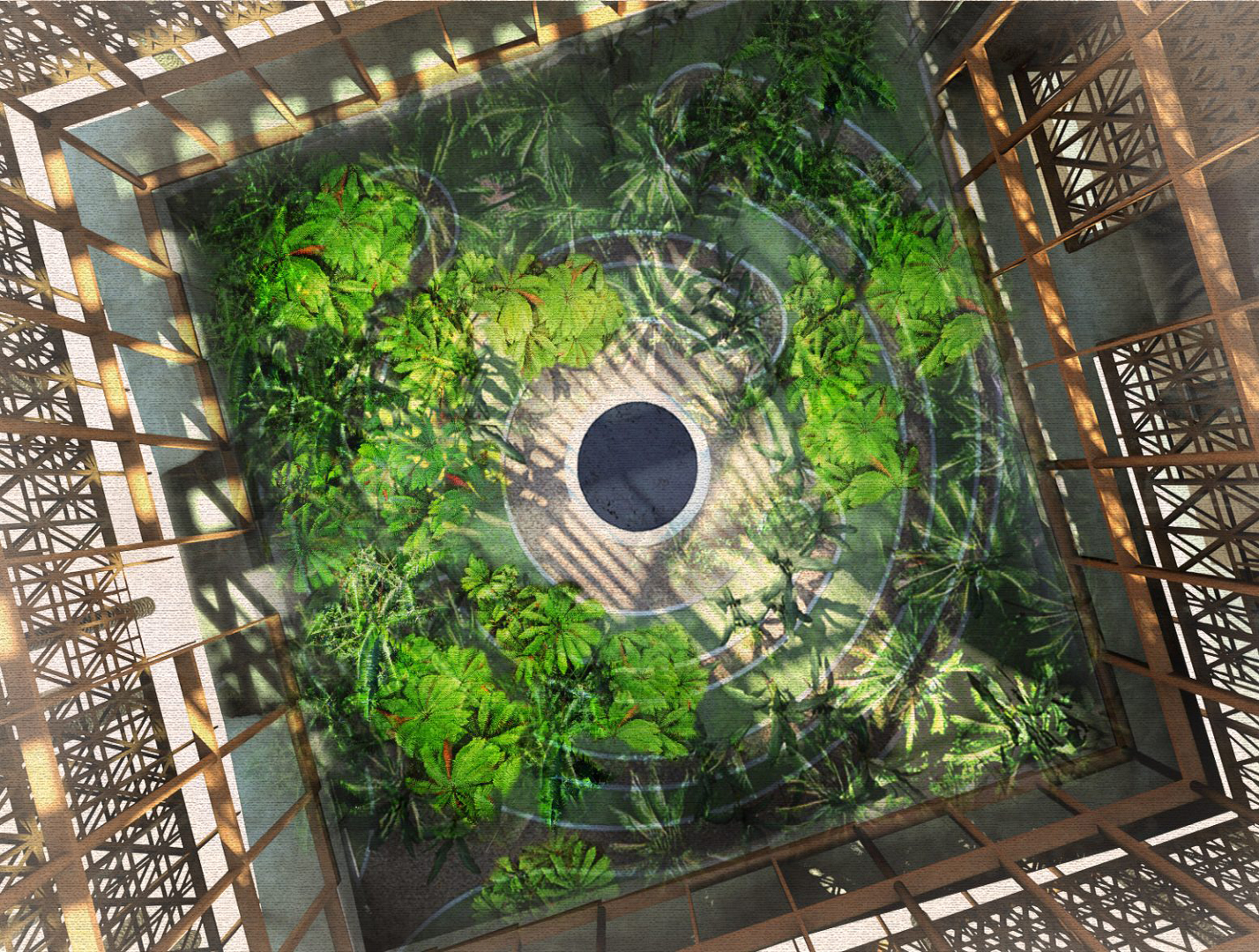

Title: Design shape of QBG Plants planned in permanent garden site.
Source: Click Here
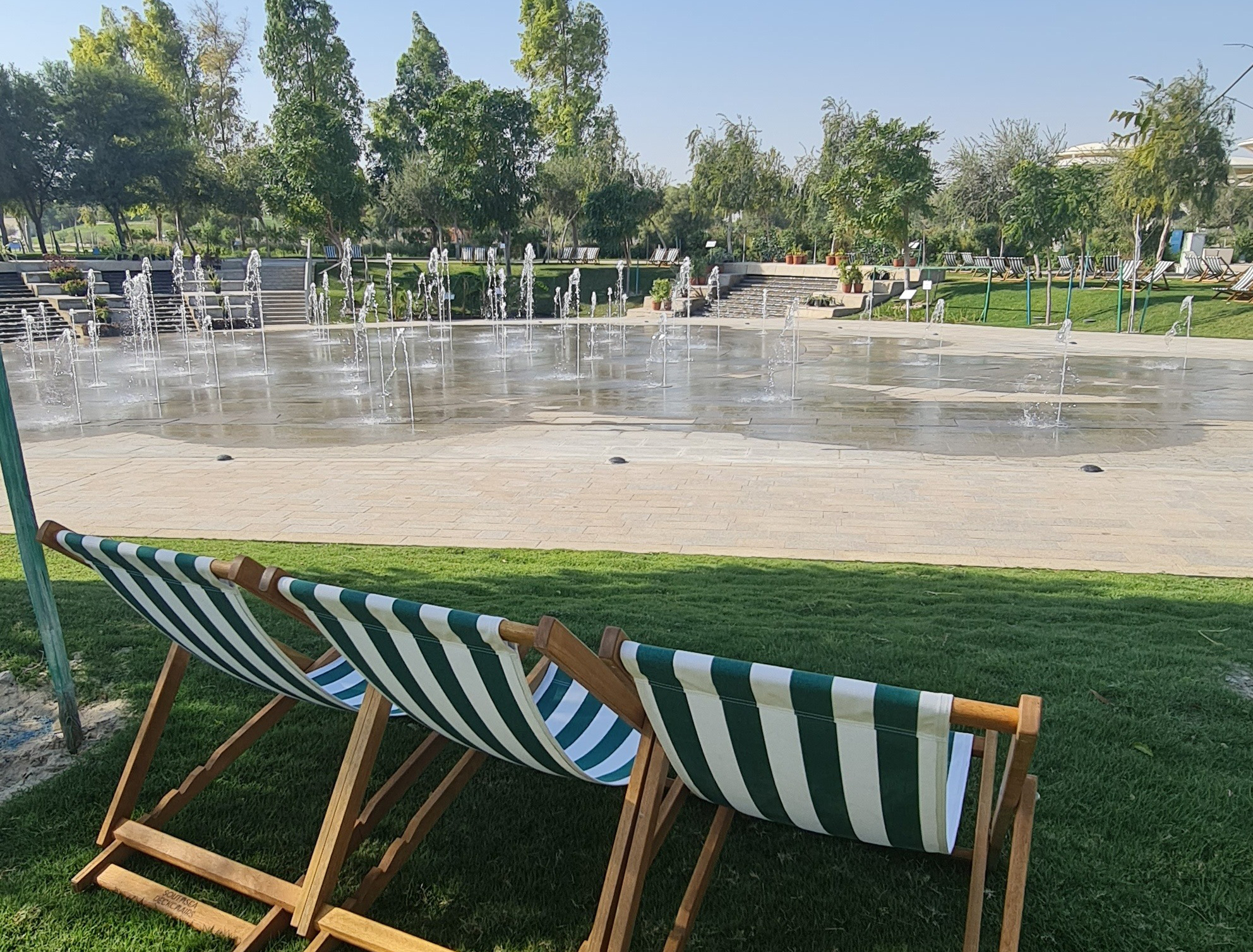

Title: Water garden with seatings.
Source: Click Here
To implement this vision, a master plan for the garden was proposed, extending over 0.4 square kilometers8 in the Al-Rayyan district of Education City, in front of the Qatar Faculty of Islamic Studies.9 The garden features the historic Al Kauthar Houses,10iii and nine key components11 with 61 plant species,12 along with two tram stations:
The project features three main programs focusing on conservation, research, and education as follows:
QBG is a global tourist attraction and a local destination for relaxation and learning.17 It integrates Islamic art and architecture, supporting academic studies and engaging the public in conservation and heritage. For instance, the garden hosts events and exhibitions to improve understanding of Islamic scriptures.18 19

Owner/Developer


Funder

Contractor/Implementer
The project was initiated and developed by the Qatar Foundation,20 previously proposed by UNESCO.21 The first seedling was planted on 17 September 2008 by Sheikha Moza bint Nasser.22 Meinhardt led the design in collaboration with Islamic theology scholars. Engineering teams with West 8 Landscape Architect and RHWL Architects created a compiled experience with strict technical standards for exhibition space and educational objectives.23 QBG was inaugurated in 2020, with further ongoing construction.24
Project Link
Endnotes
References