
Close

Approach Words: Smart Mobility, Strategic Planning, Sustainability
Public Policy Instruments: Financial Mechanism, Organization, Physical Intervention, Planning, Regulatory
The Oman National Transport Strategy 2040 is a comprehensive plan targeted at the Sultanate’s transport sector.1 Developed as a part of the Oman Vision 2040,i 2 the strategy provides a unified spatial vision both at the national level and for each governorate.3 It outlines a framework for building an advanced transport system that supports national development goals.4
This strategy aims to enhance the Sultanate’s transportation infrastructure, ensuring seamless integration among key sectors, including ports, airports, free zones, and economic areas. This integrated approach seeks to maximize commercial and investment opportunities and ensure connectivity.5
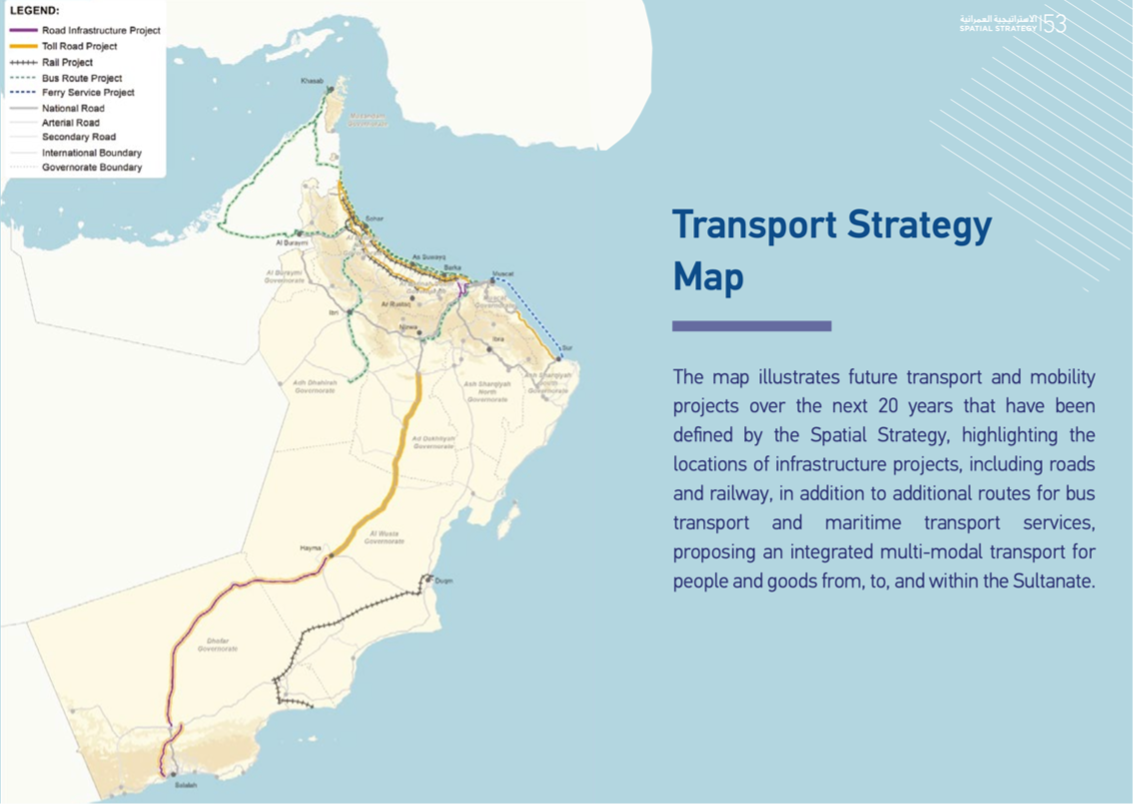
Title: Transport Strategy Map of Oman 2040
Source: Click Here

Title: Map of Greater Muscat Area highlighting roads, railways, airport, port, and business districts
Source: Click Here
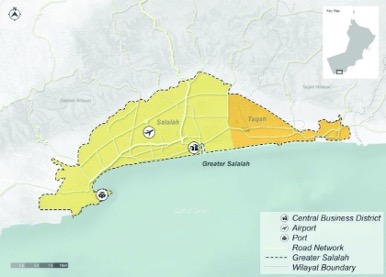
Title: A Map of Greater Salalah showing roads, railways, airport, port, and business districts
Source: Click Here

Title: A Newly Constructed Multi-Lane Highway, part of Oman Vision 2040’s Infrastructure Enhancement and Development Projects.
Source: Click Here
The National Transport Model, a key Spatial Strategy Outcome of the strategy, serves as a strategic planning tool designed to support decision making and evaluation of transport policies.6 It set a vision “to revolutionize the transportation landscape by integrating infrastructure and logistics development”.7
The National Transport Model focuses on enhancing roads, railways, ports, and airports to boost connectivity and economic growth; positioning Oman as a competitive logistics hub.8 It promotes supply chains optimization, enhanced customs procedures through digital innovation,9 10 and leverages advanced technologies such as smart systems and digital platforms for efficiency and improved user experience.11 12 The model also emphasizes on skills development of professionals through training and education;13 14 while incorporating sustainable practices, green technologies, and policies to reduce carbon emissions and promote eco-friendly transport options.15 The focus areas of the strategy include:16

Owner/Developer (Public)
Ministry of Transport, Communications and Information Technology24


Contractor/Implementer
Ministry of Transport, Communications and Information Technology27
The Strategy outlines several key targets, such as increasing the use of non-combustion energy processes from 0.5% to 62%, raising the usage of public transport from 5% to 16%, reducing daily waste generation per capita from 1.2 kg to 1 kg, and expanding the fleet of electric/hybrid vehicles to 33% for government use and 12.5% for private use.17 Transport projects will focus on the development of national highways, construction of freight rail links and light rail systems, investment in public transport in major cities, promotion of walking and cycling networks, and thebtransition to electric and hydrogen-based transport systems.18
The Strategy, led by the Ministry of Transport, Communications and Information Technology,19 involves collaboration between public and private stakeholders. Key consultancy roles are played by Aman Consultancy & Technology and Q5 (UK-based consultancy firm with an office in Muscat), among others.20 It is primarily funded by the Government of Oman with substantial contributions from private investors like the Oman Chamber of Commerce and Industry (OCCI).21
Implementation is managed by various contractors under the Ministry’s guidance, with key projects handled by local and international companies,22 and includes investment initiatives for the next 20 years, organized into four five-year plans.23
Project Link
Endnotes
References