
Close

Approach Words: Sustainability, Urban Livability, Urban Resilience
Public Policy Instruments: Financial Mechanism, Physical Intervention, Planning
The Beirut Port Recovery Plan Project is a major redevelopment initiative launched by the Lebanese government in partnership with the French government,1 following the devastating explosion at the Beirut Port in August 2020, as a resilient, safe, and efficient maritime hub.2 3
The vision behind the project is to rebuild a resilient, sustainable, and modern Beirut Port that meets international standards, ensures efficient cargo handling, and supports Lebanon’s economic recovery. of safety, and environmental responsibility.4 5
The project aims to restore the port’s infrastructure and its operations, and reposition it as a key economic and logistical hub for Lebanon and the wider region.6 It also seeks to strengthen Lebanon’s maritime trade capacity, support economic recovery, and create job opportunities, while also incorporating advanced urban planning principles to ensure integration with the surrounding neighborhoods.7 It forms part of broader national efforts to recover from the disaster and to revitalize strategic assets critical to the country’s recovery.8
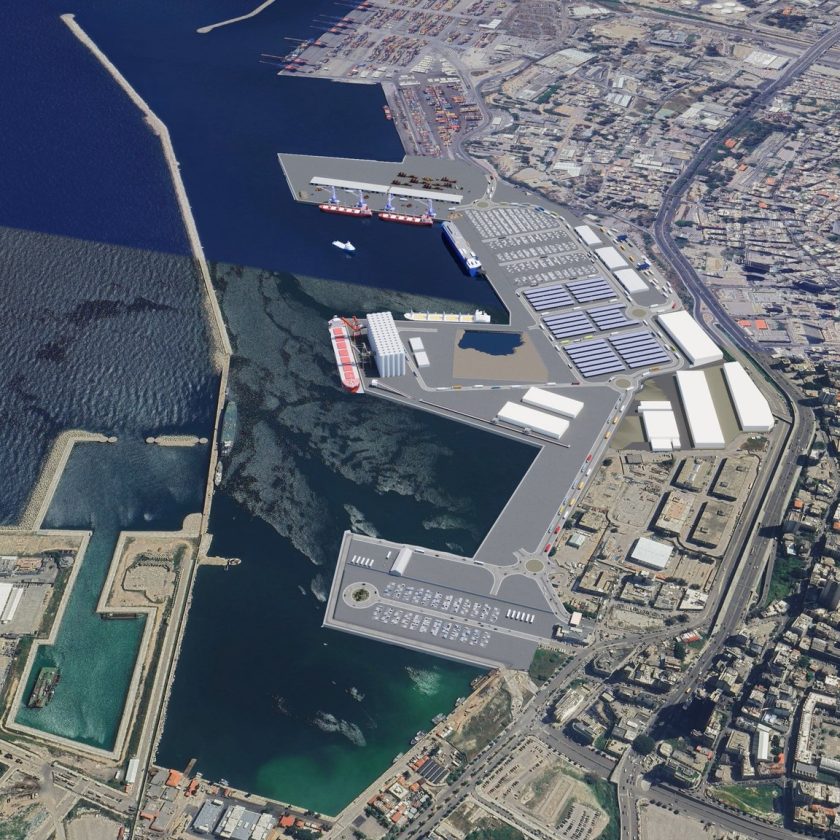

Title: 3D Showing Beirut Port Recovery Plan
Source: Click Here
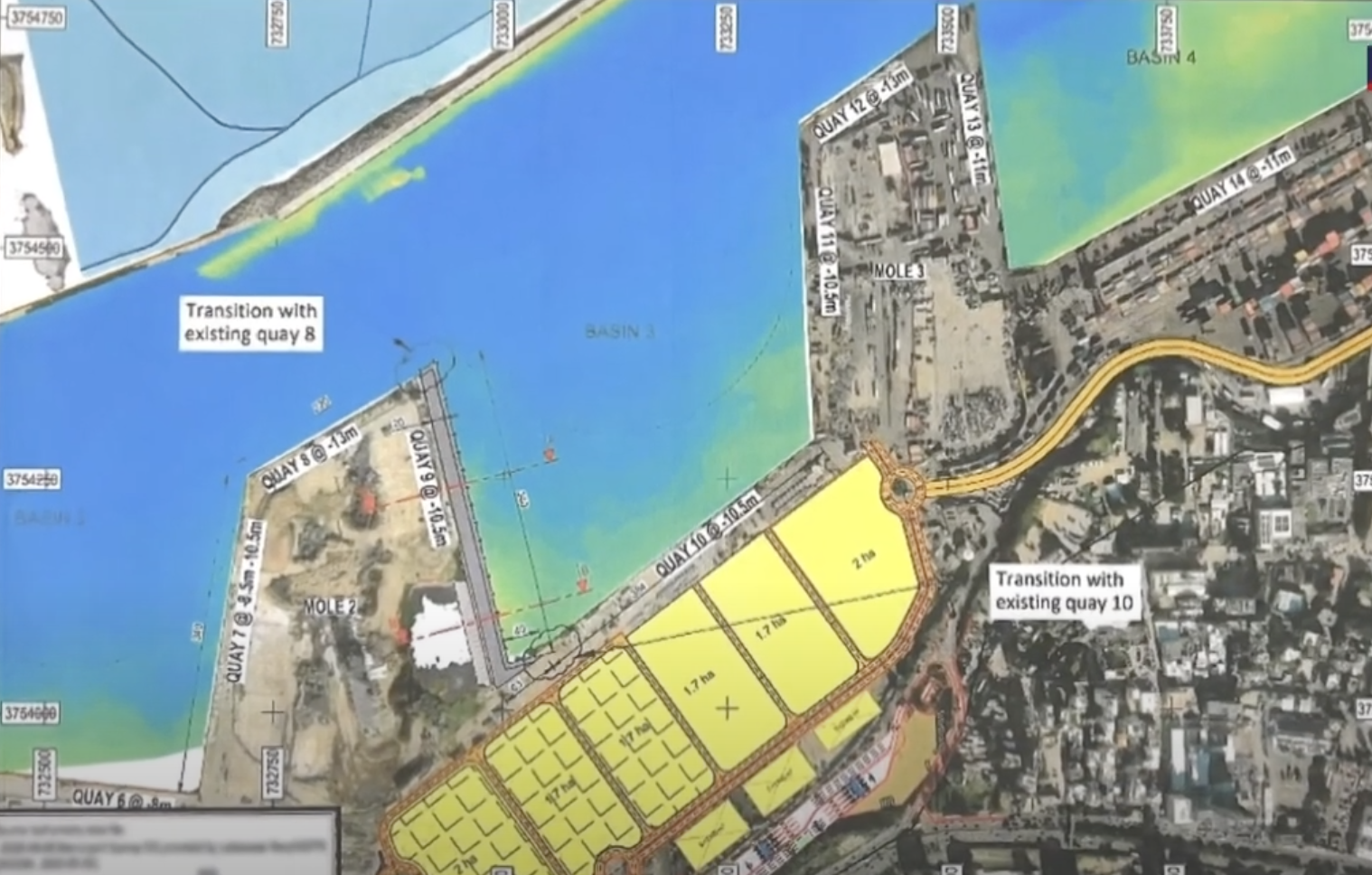
Title: Beirut Port Recovery Master Plan.
Source: Click Here
To realize the project’s vision and objectives, a comprehensive master plan was developed, encompassing three core components:9 10 11
In parallel, the master plan includes coordination with the Ministry of Economy to construct modern grain silos on approximately 25,000 square meters of allocated land. The approach preserves the historic remains of the original silos, balancing infrastructure renewal with heritage conservation.12


The Beirut Port Rehabilitation Project was commissioned by the Beirut Port Authority and the Lebanese Ministry of Transport,13 with technical support from the Port of Marseille.14 The recovery plan was designed by Artelia , a French engineering consultancy specialized in maritime infrastructure, and Egis, a global operator in transport infrastructure including roads and airports.15 Électricité de France (EDF) was also consulted to guide the renewable energy components of the plan.16 Additionally, Expertise France, the French public agency for international technical cooperation is cooperating with French and Lebanese authorities in guiding governance reform and safety upgrades.17 The final design choices and priorities were developed in close consultation with experts from the Beirut Port Authority.18
Funded by the French government,19 20 official recovery planning began early 2023, while planning and design by were finalized by March 2024.21 Reconstruction is currently in preparatory stages, with total investment is estimated at USD 60–80 million, potentially rising to USD 140 million when including private-sector asset reconstruction.22 Financing will largely come from port revenues, which reached USD 150 million in 2023, although additional international funding sources may also be pursued during the reconstruction phase.23 24 25
Project Link
Endnotes
N.A.
References