
Close

Approach Words: Efficiency, Sustainability, Urban Resilience
Public Policy Instruments: Infrastructure, Organization, Physical Intervention, Regulatory
The Al-Zawiya Combined-Cycle Power Plant is a newly developed operational power generation facility located in Az-Zāwiyah, Zawiya, Libya. 1 The project is a major advancement in Libya’s electricity infrastructure and is one of its largest combined-cycle gas turbine (CCGT) power plants, with a nameplate capacity of 1,540 Mega Watt, comprising three 480 Mega Watt units plus two 50 Mega Watt units. 2 3
The first three units were commissioned in 2007, while the fourth and fifth mobile units were commissioned in 2013, marking significant milestones for Libya’s electricity infrastructure. 4 The plant comprises three power blocks, each containing two GE GT13E2 gas turbines and one steam turbine. 5
The project aims to contribute to Libya’s electricity generation capacity as part of the national grid, with recent initiatives focused on reducing power-generation costs while enhancing energy infrastructure sustainability and reliability. 6 7
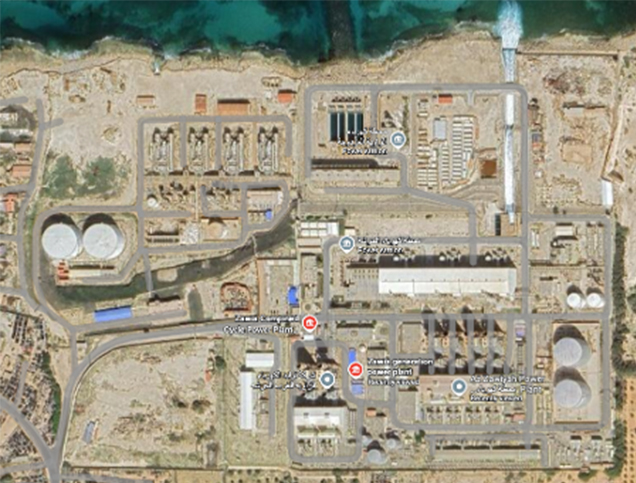

Title: Overview and Location of Al-Zawiya Combined-Cycle Power Plant.
Source: Click Here
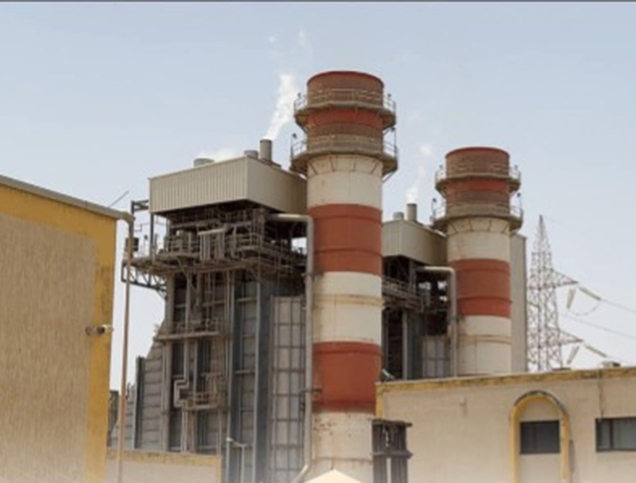

Title: Combined-cycle power generation facility at Az-Zāwiyah, Libya, showing the integration of gas and steam turbine technology for increased efficiency.
Source: Click Here
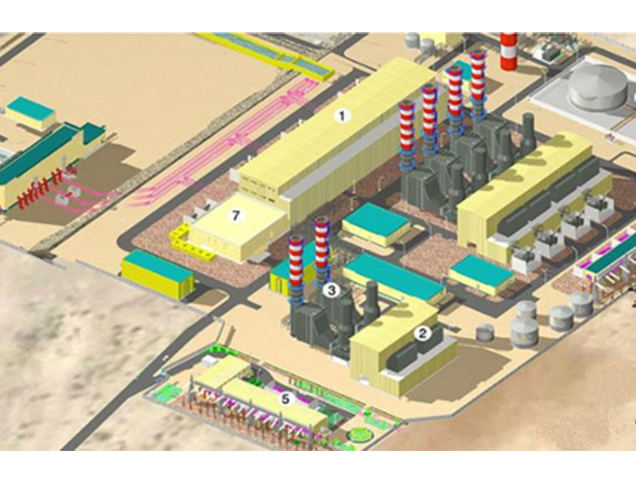

Title: Scheme of the Zawia Combined Cycle Power Plant.
Source: Click Here
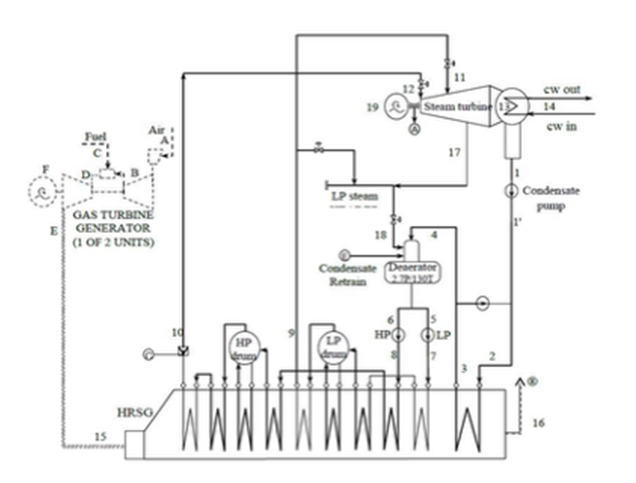
Title: Diagram of Zawia Combined Cycle Power Plant (ZCCPP).
Source: Click Here
To implement these objectives, Al-Zawiya plant operates as a dual-fuel generating unit. Natural gas is the primary fuel, with light fuel oil as a back-up in case of natural gas shortages. 8 9 The project includes key components:
Each gas turbine unit consumes about 9.263 kilograms per second of natural gas or light diesel fuel, along with 468 kilograms per second of ambient air, to produce around 155 MW of electrical energy and about 460.8 kilograms per second of exhaust gas at 585.5 degrees Celsius. 13 The plant’s turbine compressor has a pressure ratio of 14.5:1, with 21 compression stages and 5 turbine stages, operating at 3,000 revolutions per minute. 14
The overall thermal efficiency at the generator terminal is 38.6 per cent. Under ISO conditions and at an ambient temperature around 38 degrees Celsius, the efficiency is 33.6 per cent. 15 Furthermore, recent alterations to three additional steam-generation units aim to add up to around 450 Mega Watt of extra electric power, potentially available through a combined-cycle configuration without additional fuel input. 16

Owner/Developer (Public)

Consultant/Designer

The project is managed and implemented by key stakeholders including the General Electricity Company of Libya (GECOL) as the owner and operator (100% ownership). 17 18 There is ongoing collaboration between GECOL, its contractor ALGIC Energy, the steam-turbine manufacturer of Fuji Electric (Japan), and the Turkish firm ENUR, which is implementing the project. 19 The implementation of the project was divided into three phases: 20 21
Phase 1: Development of Units 1, 2, and 3, commissioned in 2007 22
Phase 2: Units 4 and 5 (mobile) installed in 2013 23
Phase 3: Integration of the three Fuji Electric 150 MW nameplate steam turbines to complete the combined cycle configuration 24
All five steam units (Units 1, 2, 3, 4-Mobile, and 5-Mobile) are currently in operation and producing power. 25 After planned overhauls of the steam units, the Al-Zawiya Combined Cycle Power Plant is expected to significantly lower the cost of power generation and enhance the sustainability and reliability of Libya’s energy infrastructure. 26
Project Link
https://www.gem.wiki/Al_Zawiya_power_station
Endnotes
References