
Close

Approach Words: Comprehensive Management, Sustainability, Urban Livability
Public Policy Instruments: Financial Mechanism, Physical Intervention, Planning, Regulatory
The Ras Girtas (Ras Laffan C) Power & Desalination Plant is a large-scale independent water and power project (IWPP) located in Ras Laffan Industrial City, about 80 kilometers north of Doha, Qatar.1 It is one of the world’s most powerful dual-utility facilities, designed to simultaneously produce electricity and desalinated water at industrial scale.2
The project’s vision is “to enhance Qatar’s energy and water security” by providing reliable base-load electricity and potable water to meet rapidly growing national demand.3 It aims to generate 2,730 MW of electricity, produce 63 million imperial gallons per day of desalinated water, and reduce pressure on national energy and water systems while ensuring efficiency and resilience.4 5
Title: Location of Ras Gitras Power and Desalination Plant within Qatar
Source: Click Here
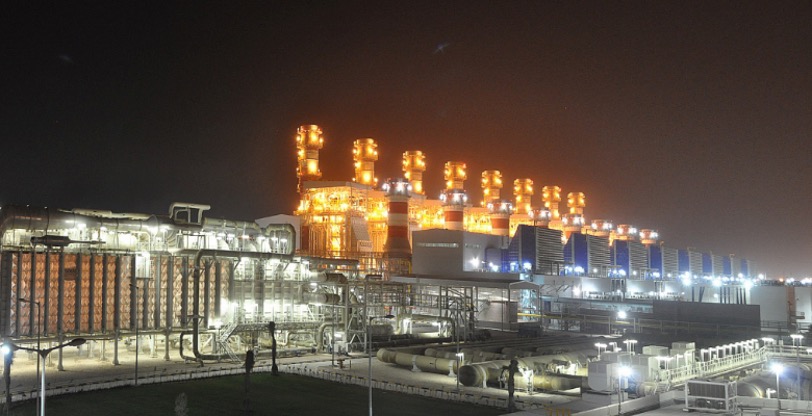

Title: Qatar Ras Laffan C thermal power and desalination facility.
Source: Click Here
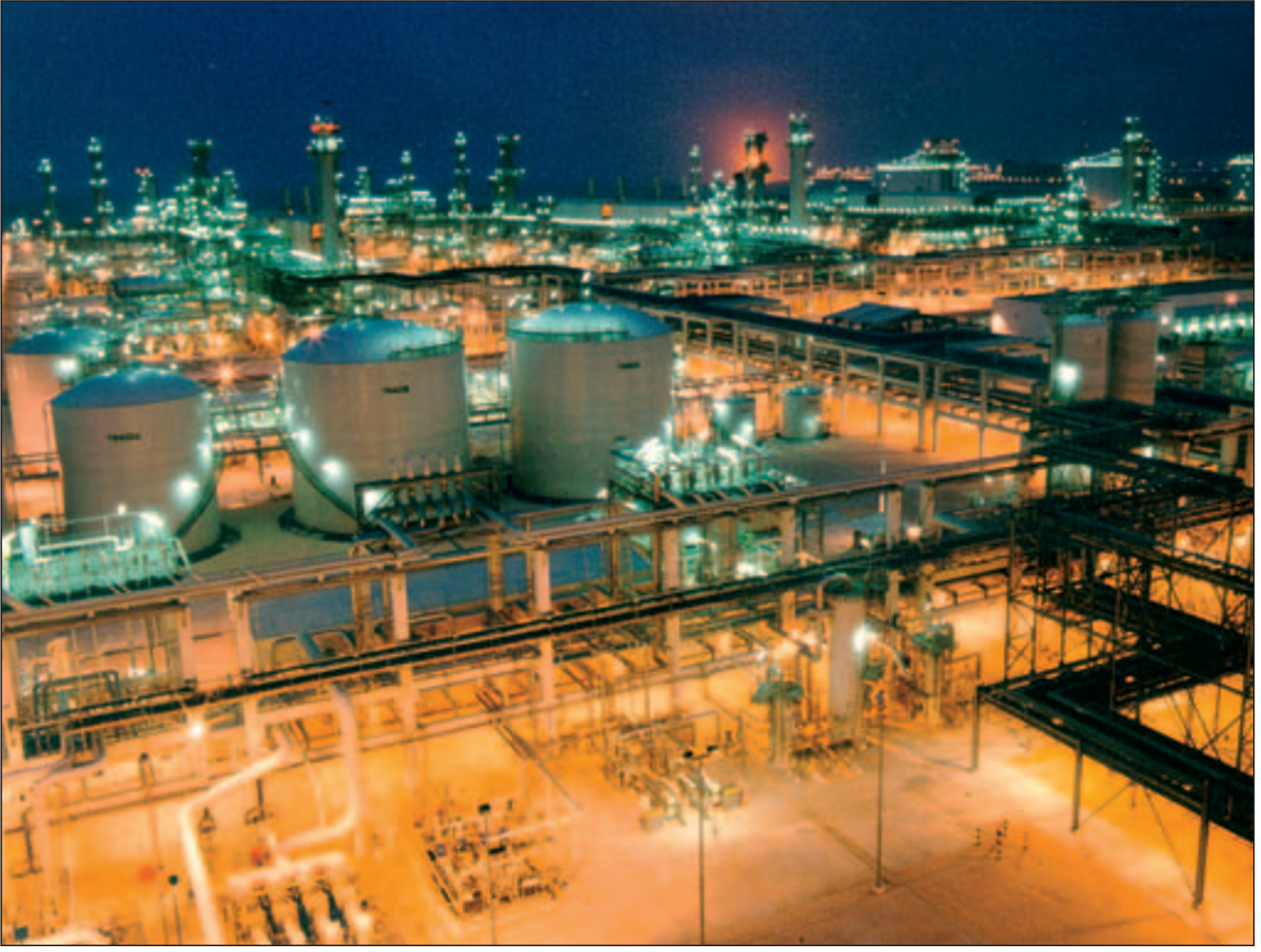

Title: Ras Laffan C power and water plant.
Source: Click Here
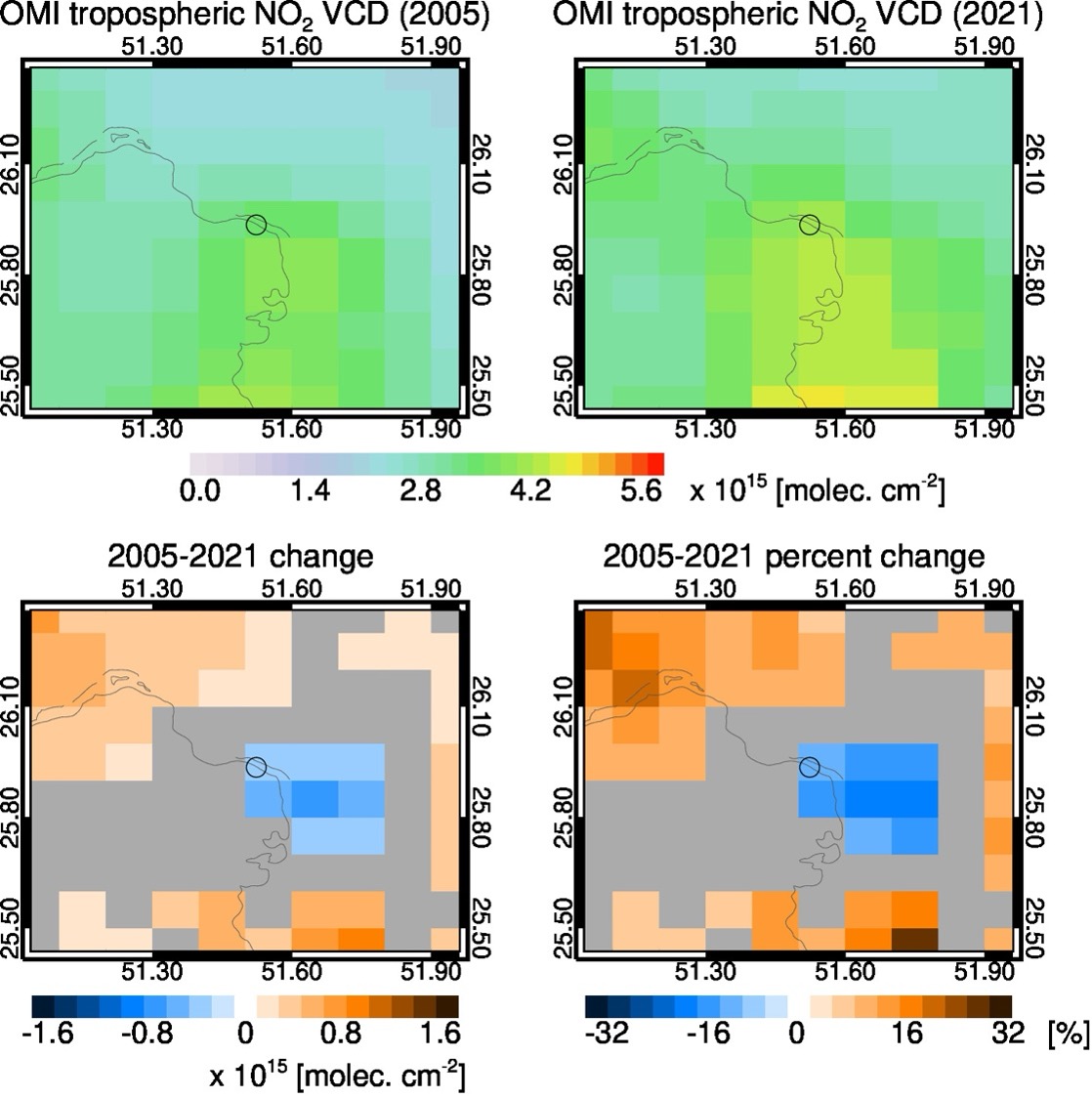
Title: Ras Laffan C combined-cycle gas turbine (CCGT) power plant OMI records from 2005 to 2021.
Source: Click Here
To implement the vision, the project was developed under a 25-year Build-Own-Operate-Transfer (BOOT) Power and Water Purchase Agreement (PWPA) with the General Electricity and Water Corporation (Kahramaa).6 7 The plant employs combined-cycle gas turbines for electricity generation and multi-effect distillation/thermal vapor compression (MED/TVC) units for desalination, achieving high efficiency and low emissions.8 At commissioning, the facility accounted for about 30% of Qatar’s electricity supply and around 17-18% of its water production.9
The integrated design brings together eight Mitsubishi M701F3 gas turbines, four TC2F-30 steam turbines, and ten SIDEM multi-effect distillation units.10 The project cost approximately USD 3.5 billion and was financed through Qatar Petroleum (now QatarEnergy), the Japan Bank for International Cooperation (JBIC), 20 international commercial banks, Qatar National Bank (QNB), and Qatar Islamic Bank (QIB).11
The Ras Girtas project represents Qatar’s commitment to sustainability and efficiency by maximizing dual-utility generation in a single footprint.12 13 This approach reduces environmental impact, optimizes fuel use, and establishes strategic reserve capacity.14 15 Its scale and integration also demonstrate international collaboration and the transfer of advanced energy and desalination technologies into the Qatari context.16 17

Owner/Developer

The project is owned and operated by Ras Girtas Power Company,i 18 19 whose shareholders are Qatar Electricity & Water Company (45%), Qatar Petroleum/QatarEnergy (15%), ENGIE/GDF Suez (20%), Mitsui (10%), Chubu Electric (5%), and Shikoku Electric (5%).20 21 EPC and construction contractors included Mitsui, Hyundai Engineering & Construction, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, SIDEM, and Doosan.22 23
The project contract was awarded in March 2008.24 Construction was completed in record time of about three years, with the first phase in 2010 supplying 1,833 MW to the grid.25 The facility was fully commissioned and inaugurated on May 31, 2011, by the Emir of Qatar.26 The BOOT contract ensures a 25-year operational period before transfer to the state utility.27
Project Link
Endnotes
References