
Close

Approach Words: Comprehensive Management, Sustainability, Urban Resilience
Public Policy Instruments: Financial Mechanism, Physical Intervention, Planning, Regulatory
The Askar Waste-to-Energy Project, located at the Askar landfill site in Southern Bahrain,1 is a pioneering initiative that aims to convert solid waste into energy, thereby extending the operational life of the Askar landfill and offering a renewable source of power.2
The vision of the Askar Waste-to-Energy Project is to “establish a sustainable waste management system that efficiently manages municipal solid waste and generates renewable energy”.3 The project seeks to treat 390,000 tons of solid waste annually through incineration, generating 25 MW of power to be fed into the national grid.4 This approach aims to ease solid waste management in Manama, the capital city, while offering an alternative method for generating power nationwide.5 6
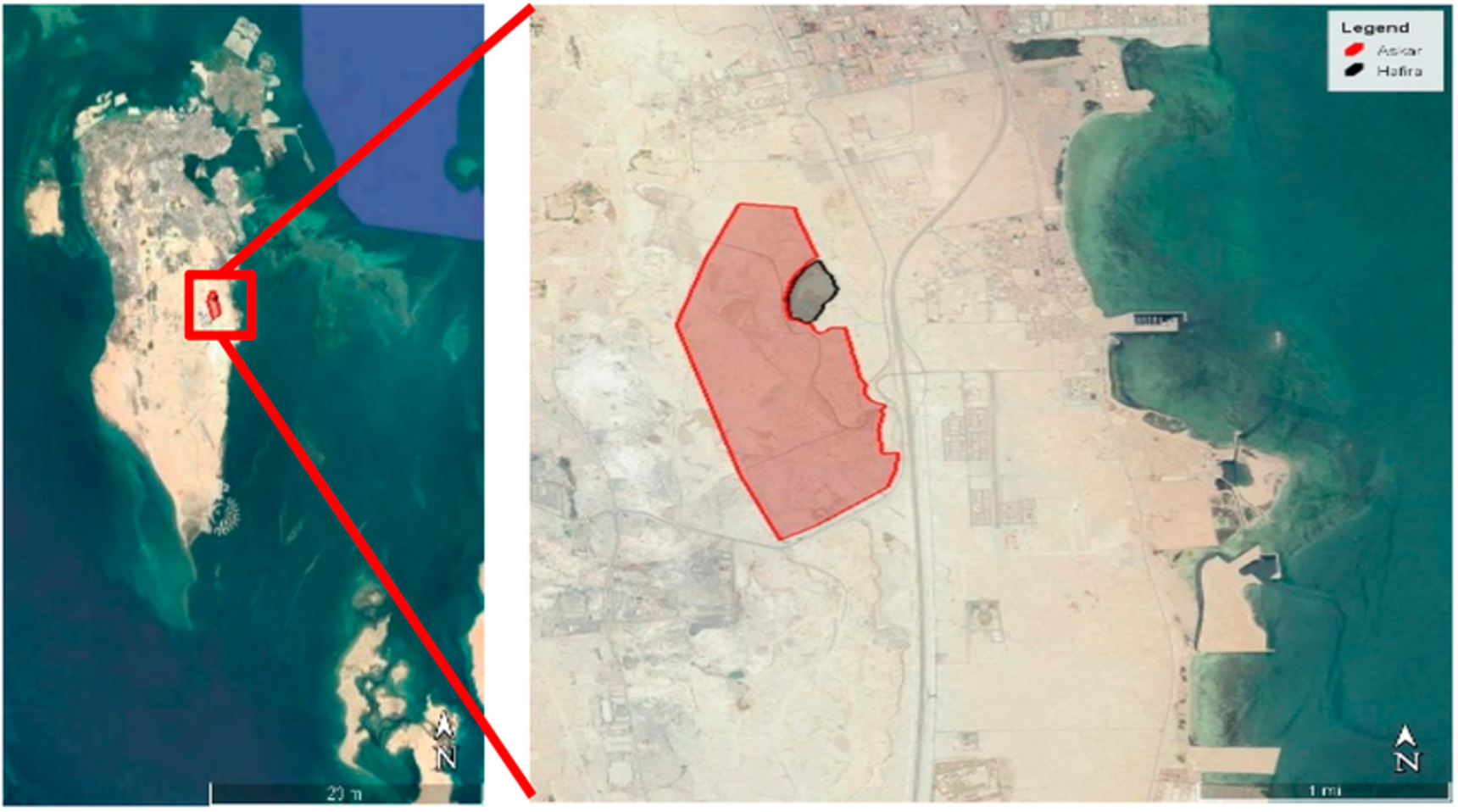
Title: The position of Askar within Bahrain.
Source: Click Here

Title: Askar Landfill, the all-time primary dump site for the wastes in Bahrain.
Source: Click Here
To implement this vision, the project is structured as a Public-Private Partnership (PPP) venture operating under a Build-Operate-Transfer (BOT) model.7 This collaborative framework involves collaboration between the Bahrain government and private companies, utilizing landfill gas extraction and incineration technology to release stored energy from municipal solid waste.8 9
The project emphasizes values such as environmental sustainability, resource conservation, and public health protection. By transforming waste into energy, the Askar Waste-to-Energy Project will reduce waste volume, generate renewable energy, and mitigate the environmental impact of waste disposal.10 11
The master plan will emphasize the deployment of advanced waste treatment technologies, promoting collaboration between public and private sectors, and ensuring strict compliance with environmental regulations. This integrated approach will enhance waste management efficiency and contribute to Bahrain’s sustainable development goals.12 13
The primary beneficiaries of the Askar Waste-to-Energy Project are the residents of Bahrain, particularly those in the capital city, Manama. The project will improve waste management, reduce environmental pollution, and provide a reliable source of renewable energy, benefiting both locals and the broader community.14 15

Owner/Developer (Public)

Consultant/Designer
Developed under a Public-Private Partnership (PPP) model, with financing arranged by the French developer Cnim,16 the project is owned by Bahrain’s Ministry of Works, Municipalities Affairs and Urban Planning, private waste management contractors, and UK-based consultancy firms.17 18
The Askar Waste-to-Energy Project, currently at the announced stage, will begin construction in 2025 and is expected to start commercial operations by 2026.19 20 The project will operate under a 25-year BOT contract, with ongoing monitoring and evaluation to ensure compliance with environmental and operational standards.21 22
Project Link
Endnotes
N.A.
References