
Close

Approach Words: Environment Preservation, Sustainability, Urban Livability
Public Policy Instruments: Organization, Physical Intervention, Planning, Regulatory
The Cairo Greenbelt Project is a large-scale environmental development initiative. This ambitious project aims to combat air pollution, mitigate desert encroachment, and promote sustainable urban development in Greater Cairo, covering parts of the Cairo, Giza, and Qalyubia governorates.1 The project was initiated in 2005 as part of Egypt’s broader strategy to enhance urban sustainability and ecosystem resilience.2 It envisions a “green belt around Cairo that acts as a windbreak against desert dust, reduces pollution, and utilizes treated wastewater for irrigation”.3
The primary objectives of the Cairo Greenbelt Project include reducing air pollution around Greater Cairo, enhancing the city’s greenery, and utilizing treated wastewater. In addition to creating job opportunities, generating economic returns through maintenance and timber production, as well as protecting public health by reducing respiratory diseases caused by dust and pollution.4 5

Title: Map illustrating the Greenbelt encircling Cairo.
Source: Click Here
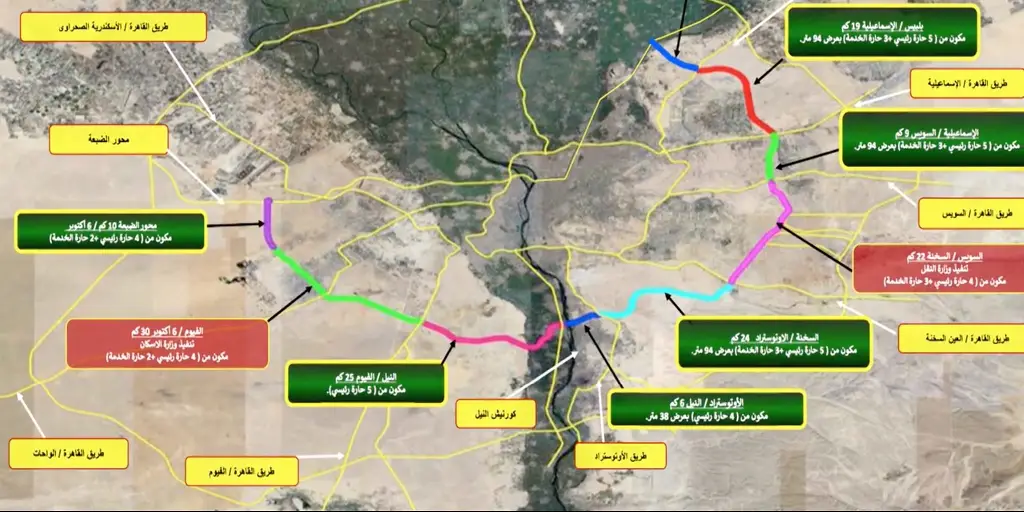
Title: Distribution of designated Greenbelt regions surrounding Cairo
Source: Click Here
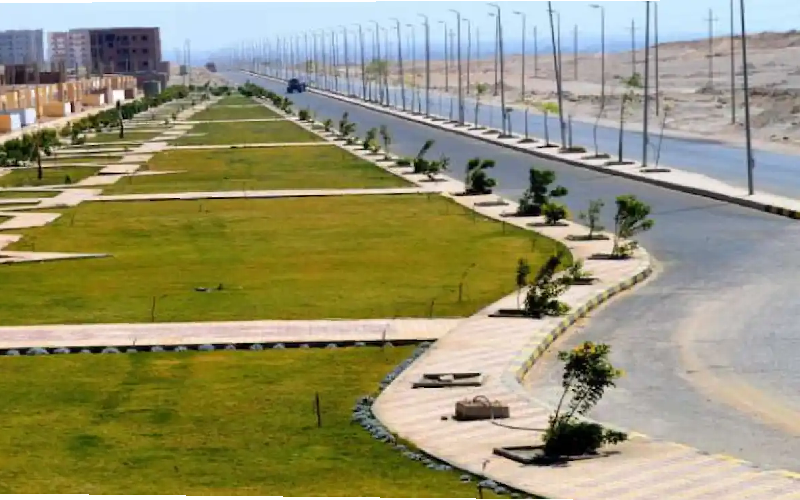

Title: Part of the implemented Greenbelt in 6th of October City, part of Greater Cairo
Source: Click Here

Title: Public spaces within the Zayed City area, located inside the Greenbelt zone.
Source: Click Here
To implement these objectives, the Cairo Greenbelt Project extends 100 kilometers around the city,6 consisting of 2 phases. Phase one includes 50 kilometers in Cairo Governorate, 28 kilometers in Giza, and 22 kilometers in Qalyubia. Phase 2 involves planting trees along cross-sectional roads, extending 25 kilometers on either side of Cairo’s Ring Road.7 8 The following are core components of the project:

Owner/Developer (Public)

Environmentally, the Cairo Greenbelt Project is a model of sustainability, aligning with global afforestation and climate adaptation efforts through urban greening initiatives. In addition to this, it is also a part of a larger regional strategy, where similar greenbelt initiatives have been launched in Syria, Jordan, Algeria, Iraq, and Sudan.19 These collective efforts aim to combat desertification, promote sustainable development, enhance the green economy, and address the adverse effects of climate change.20
The project is a collaboration between Egypt’s Ministry of Environment, which oversees the project, and the Armed Forces, which are responsible for tree planting and ongoing maintenance. The first phase, launched in 2005, successfully planted 65,000 trees over 22 kilometers, using well-suited species to the region’s climate and environmental needs.21 22
Project Link
Endnotes
N.A.
References