
Close

Approach Words:
Public Policy Instruments:
The Strategy for Accelerated Growth and Shared Prosperity (SCAPP) is Mauritania’s long-term national development framework, initiated in 2016 and spanning through 2030. 1 It addresses economic transformation, human capital development, and governance across all 13 regions and 219 municipalities. 2
Th SCAPP envisions “higher, sustainable, and more inclusive growth and job creation, development of human capital, improving access to basic social services, and strengthened governance.” 3 4
SCAPP aims to achieve sustainable and inclusive development across Mauritania. 5 It serves as a national development roadmap to reduce regional disparities and integrate international development frameworks, such as SDGs and Agenda 2063, into national planning. 6 The strategy focuses particularly on geographic, social, and economic inequalities in vulnerable regions like Hodh Chargui. 7
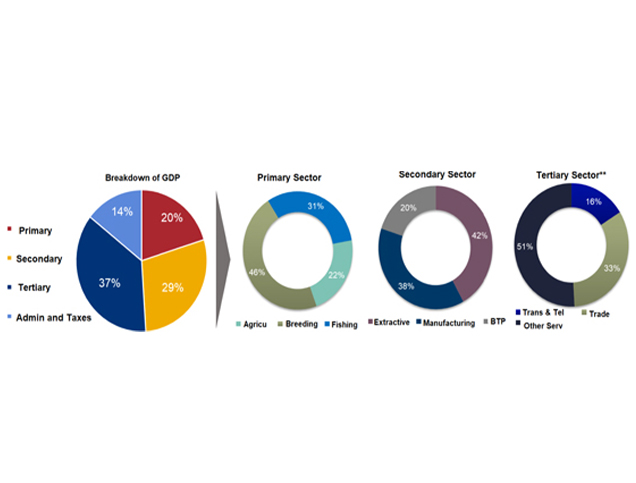
Title: Analysis of the distribution of the country GDP.
Source: Click Here
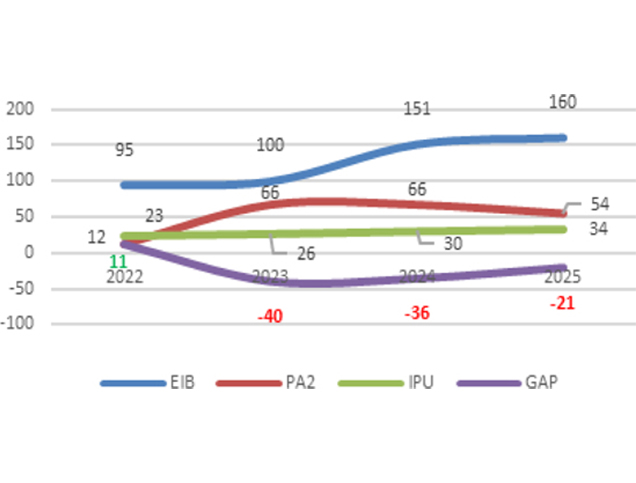
Title: Estimated funding gap for PA2 SCAPP in billions of MRU.
Source: Click Here
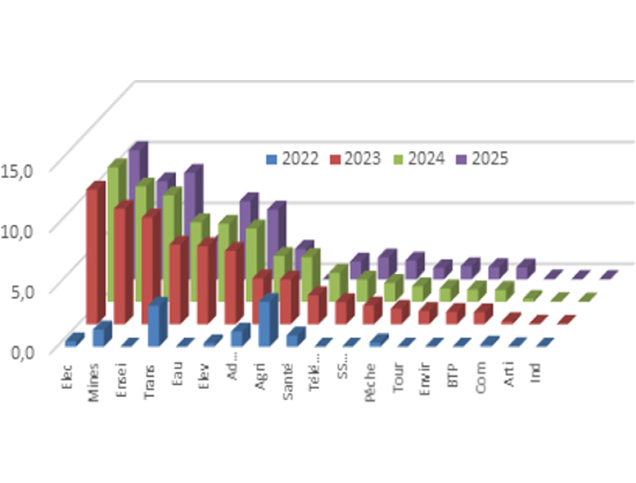
Title: Financial programming by branch and year in billions of.
Source: Click Here
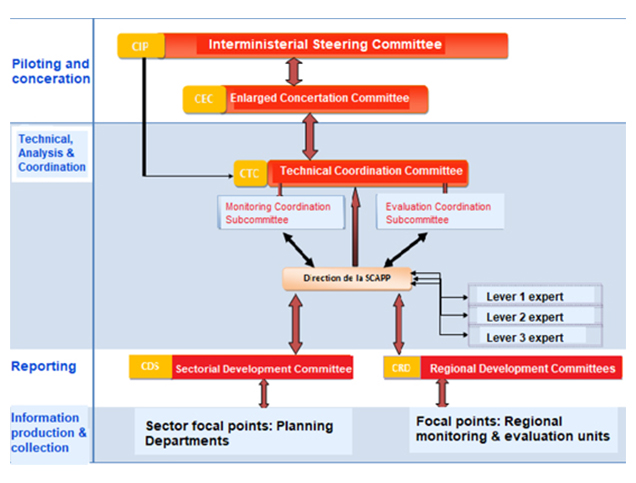
Title: The institutional levels of the organization.
Source: Click Here
To implement the vision, SCAPP is operates through rolling five-year action plans, 8 including specifically the following components:
The SCAPP is built on principles of decentralization, participation, sustainability, inclusivity, and environmental sustainability. Local populations and authorities are directly involved in planning, implementation, and monitoring the development policies 14 tailored to local contexts. Additionally, sustainability is further emphasized through alignment with Mauritania’s National Strategy for the Environment and Sustainable Development (SNEDD), which vision is 15 preserved environment at the service of sustainable development.” 16


Owner/Developer

Contractor/Implementer
The SCAPP is led by Mauritania’s Ministry of Economy and Finance, under the oversight of the Prime Minister’s office. 17 Coordination is managed through a multi-level structure that includes Inter-ministerial Steering Committee (CIP) chaired by the Prime Minister; 18 the Enlarged Consultation Committee, chaired by the Minister of Economy and Finance and involving civil society and other stakeholders; 19 and the SCAPP Coordination and Monitoring Committee (CCS-SCAPP), chaired by the Director General of Development Policies and Strategies. 20 Key development partners supporting SCAPP include the UN Economic Commission for Africa (ECA), which provides technical assistance; 21 the World Bank, which contributed analytical insights through its Systematic Country Diagnostic (SCD); 22 and the African Development Bank, whose country strategy is closely aligned with the SCAPP’s Second Action Plan (PA2). 23
The SCAPP implementation over phases:
· Phase 1 (2016-2020): Strategic frameworks, baseline development, and initial action plan,
· Phase 2 (2021-2025): Second action plan, under implementation, 24 including regional pilot project (SCRAPP); emphasizes expansion, regionalization, and more inclusive development policies.
· Hodh Chargui pilot launch: June 2020, with initial evaluation September 2020. 25
Further work needed on nationalizing SDG targets and indicators, especially per the 2019 Voluntary National and UCLG recommendations. 26
Project Link
Endnotes
References